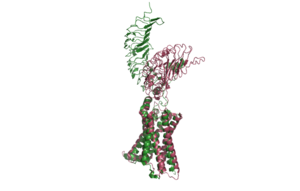We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1792
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Structure== | == Structure== | ||
TSHR forms a complex with TSH and G<sub>s</sub> proteins. This is called the <scene name=scene name='95/952720/Tsh-tshr-gs_complex/3'>TSH-TSHR-Gs Complex</scene>. | TSHR forms a complex with TSH and G<sub>s</sub> proteins. This is called the <scene name=scene name='95/952720/Tsh-tshr-gs_complex/3'>TSH-TSHR-Gs Complex</scene>. | ||
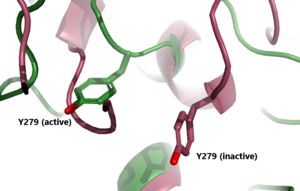
| - | <scene name=scene name='95/952720/Structure_overview_spins/3'>TSHR has 3 main domains</scene>: Leucine Rich Region Domain (coral), the hinge region (blue-purple), and the transmembrane region(rainbow). The leucine rich region domain is extracellular. This is where TSH will bind. The hinge region is also extracellular. Conformational changes in this region are responsible for the switch between the active vs inactive state. Finally, the transmembrane region is located within the plasma membrane. Its function is to hold the receptor into the membrane. This domain is also bound to the [ | + | <scene name=scene name='95/952720/Structure_overview_spins/3'>TSHR has 3 main domains</scene>: Leucine Rich Region Domain (coral), the hinge region (blue-purple), and the transmembrane region(rainbow). The leucine rich region domain is extracellular. This is where TSH will bind. The hinge region is also extracellular. Conformational changes in this region are responsible for the switch between the active vs inactive state. Finally, the transmembrane region is located within the plasma membrane. Its function is to hold the receptor into the membrane. This domain is also bound to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein G-proteins] at the N-terminus. The G-proteins are located on the intracellular side of the plasma membrane. They are important for transmitting the binding signal into the cell, setting off a protein signaling cascade. |
=== Transmembrane Region=== | === Transmembrane Region=== | ||
<scene name='95/952720/Transmembrane_region_spin/5'>The Transmembrane Region</scene> (<scene name='95/952720/Transmembrane_region_top-view/2'>top-view</scene>) is embedded within the cell membrane. Like other G-protein receptors, it is made up of a 7-pass helix <ref name="Faust"> DOI 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1</ref>. It is made up of about 284 residues. The transmembrane region is surrounded by a "belt" of <scene name='95/952720/Tmd_cholesterol_spin/2'>15 cholesterols</scene>. When cholesterol binding sites are mutated such that they are unfunctional, TSHR activity decreases. Thus, the cholesterols are important for TSHR function <ref name="Duan"> DOI 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3</ref>. Additionally, at the N-terminus, the transmembrane region binds to the <scene name='95/952720/Transmembrane_region_spin/4'>G-proteins</scene>, which are located intracellularly. | <scene name='95/952720/Transmembrane_region_spin/5'>The Transmembrane Region</scene> (<scene name='95/952720/Transmembrane_region_top-view/2'>top-view</scene>) is embedded within the cell membrane. Like other G-protein receptors, it is made up of a 7-pass helix <ref name="Faust"> DOI 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1</ref>. It is made up of about 284 residues. The transmembrane region is surrounded by a "belt" of <scene name='95/952720/Tmd_cholesterol_spin/2'>15 cholesterols</scene>. When cholesterol binding sites are mutated such that they are unfunctional, TSHR activity decreases. Thus, the cholesterols are important for TSHR function <ref name="Duan"> DOI 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3</ref>. Additionally, at the N-terminus, the transmembrane region binds to the <scene name='95/952720/Transmembrane_region_spin/4'>G-proteins</scene>, which are located intracellularly. | ||
Revision as of 17:24, 7 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
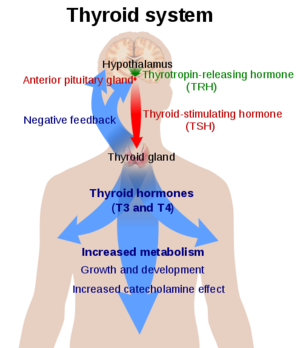
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor (TSHR)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Faust B, Billesbolle CB, Suomivuori CM, Singh I, Zhang K, Hoppe N, Pinto AFM, Diedrich JK, Muftuoglu Y, Szkudlinski MW, Saghatelian A, Dror RO, Cheng Y, Manglik A. Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. PMID:35940205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Duan J, Xu P, Luan X, Ji Y, He X, Song N, Yuan Q, Jin Y, Cheng X, Jiang H, Zheng J, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Xu HE. Hormone- and antibody-mediated activation of the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. PMID:35940204 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3
- ↑ Chen CR, McLachlan SM, Rapoport B. Thyrotropin (TSH) receptor residue E251 in the extracellular leucine-rich repeat domain is critical for linking TSH binding to receptor activation. Endocrinology. 2010 Apr;151(4):1940-7. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1430. Epub 2010 Feb 24. PMID: 20181794; PMCID: PMC2851189. [DOI 10.1210/en.2009-1430 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2851189/]
Student Contributors
- Alex Kem
- Grace Lane