Sandbox Reserved 1791
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
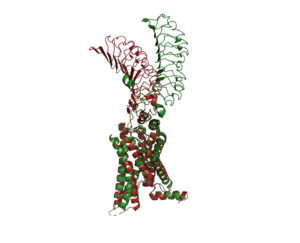
[[Image:Image-Inactive Inactive Proteopedia.png|300 px|right|thumb| An overview of the Inactive (red) vs Active (green) state of TSHR. PDB: 7WX5]] | [[Image:Image-Inactive Inactive Proteopedia.png|300 px|right|thumb| An overview of the Inactive (red) vs Active (green) state of TSHR. PDB: 7WX5]] | ||
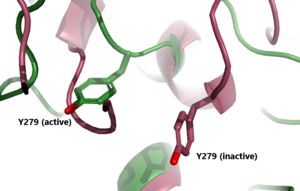
[[Image:Inactive v active residue.png|300 px|right|thumb| Figure 3: A zoomed in view of the Y279 residue in the Hinge Region of TSHR, showing the 6 angstrom move of Y279 during the activation of TSHR. Active TSHR is shown in green (PDB: 7t9i) and inactive TSHR is shown in pink (PDB: 7t9m).]] | [[Image:Inactive v active residue.png|300 px|right|thumb| Figure 3: A zoomed in view of the Y279 residue in the Hinge Region of TSHR, showing the 6 angstrom move of Y279 during the activation of TSHR. Active TSHR is shown in green (PDB: 7t9i) and inactive TSHR is shown in pink (PDB: 7t9m).]] | ||
| - | When TSHR is not bound to TSH, it is in the <scene name='95/952720/Inactivetshr/7'>inactive state</scene>. This is also considered the "down" state because the LRRD is pointing down. When TSH binds to TSHR, steric clashing between TSH and the cell-membrane cause TSHR to take on the <scene name='95/952720/Inactivetshr/6'>active or "up" state</scene>. During this transition, the Extracellular domains rotate 55° along an axis. This rotation is caused by conformational changes within the <scene name='95/952720/Hinge_region_spin/1'>Hinge Region</scene>, specifically at the <scene name='95/952720/Hinge_region_residues/2'>Y279 residue</scene>. This residue moves 6 angstroms relative to I486, which is a residue located in the Transmembrane Region <ref name="Faust"/> | + | When TSHR is not bound to TSH, it is in the <scene name='95/952720/Inactivetshr/7'>inactive state</scene>. This is also considered the "down" state because the LRRD is pointing down. When TSH binds to TSHR, steric clashing between TSH and the cell-membrane cause TSHR to take on the <scene name='95/952720/Inactivetshr/6'>active or "up" state</scene>. During this transition, the Extracellular domains rotate 55° along an axis. This rotation is caused by conformational changes within the <scene name='95/952720/Hinge_region_spin/1'>Hinge Region</scene>, specifically at the <scene name='95/952720/Hinge_region_residues/2'>Y279 residue</scene>. This residue moves 6 angstroms relative to I486, which is a residue located in the Transmembrane Region <ref name="Faust"/>. The active form is found when <scene name='95/952719/Active_form/4'>TSHR is bound to TSH or M22</scene>. The structure can be seen as straight. The inactive form is found when <scene name='95/952719/Inactive_form/6'>TSHR is bound with K1</scene> of TSHR is found when bound with K1. The overall structure of the molecule is bent when K1 is bound. |
| - | + | ||
| - | The active form is found when <scene name='95/952719/Active_form/4'>TSHR is bound to TSH or M22</scene>. The structure can be seen as straight. The inactive form is found when <scene name='95/952719/Inactive_form/6'>TSHR is bound with K1</scene> of TSHR is found when bound with K1. The overall structure of the molecule is bent when K1 is bound. | + | |
== Specific Residues and Interactions== | == Specific Residues and Interactions== | ||
Revision as of 17:27, 7 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor (TSHR)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Faust B, Billesbolle CB, Suomivuori CM, Singh I, Zhang K, Hoppe N, Pinto AFM, Diedrich JK, Muftuoglu Y, Szkudlinski MW, Saghatelian A, Dror RO, Cheng Y, Manglik A. Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. PMID:35940205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1
- ↑ Chen CR, McLachlan SM, Rapoport B. Thyrotropin (TSH) receptor residue E251 in the extracellular leucine-rich repeat domain is critical for linking TSH binding to receptor activation. Endocrinology. 2010 Apr;151(4):1940-7. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1430. Epub 2010 Feb 24. PMID: 20181794; PMCID: PMC2851189. [DOI 10.1210/en.2009-1430 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2851189/]
- ↑ Duan J, Xu P, Luan X, Ji Y, He X, Song N, Yuan Q, Jin Y, Cheng X, Jiang H, Zheng J, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Xu HE. Hormone- and antibody-mediated activation of the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. PMID:35940204 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3
- ↑ Fokina, E.F., Shpakov, A.O. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor: the Role in the Development of Thyroid Pathology and Its Correction. J Evol Biochem Phys 58, 1439–1454 (2022). [DOI:10.1134/S0022093022050143 https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093022050143]
- ↑ Smits G, Govaerts C, Nubourgh I, Pardo L, Vassart G, Costagliola S. Lysine 183 and glutamic acid 157 of the TSH receptor: two interacting residues with a key role in determining specificity toward TSH and human CG. Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Apr;16(4):722-35. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.4.0815. PMID: 11923469. [DOI: 10.1210/mend.16.4.0815 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11923469/]
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Chiovato L, Magri F, Carlé A. Hypothyroidism in Context: Where We've Been and Where We're Going. Adv Ther. 2019 Sep;36(Suppl 2):47-58. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01080-8. Epub 2019 Sep 4. PMID: 31485975; PMCID: PMC6822815. [DOI: 10.1007/s12325-019-01080-8 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31485975/]
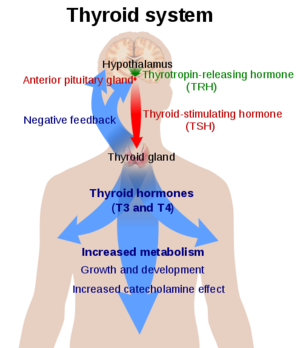
![(Fig. 3) TSH’s role in the diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism: [1]](/wiki/images/thumb/9/95/TSH_role.jpeg/400px-TSH_role.jpeg)
