Introduction
(SMP) is a 3-subunit complex essential for cell proliferation and the survival of many cancers[1] and RASopathies.[2] The SMP holophosphatase complex functions as a key regulator of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling pathway by removing an inhibitory phosphate on the RAF family of proteins to allow for MAPK signaling.[2] This interaction of the RTK-Ras pathway and the SMP complex drives cell proliferation.[1] The SMP complex is made of three subunits, SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. Each of these subunits has a different shape that corresponds to its different function. The SHOC2 subunit uses a crescent shape to enhance substrate interactions and complex stability.[3] PP1C is a phosphatase, and this subunit contains the catalytic site of the complex which dephosphorylates the N-terminal phosphoserine (NTpS) of RAF green link here.[3] The MRAS subunit binds to GTP which triggers assembly of the SMP complex. The C-terminus of the MRAS subunit localizes the complex to the cell membrane.[3] Mutations in one or multiple of these subunits leads to over-activation of the signaling pathway, which may result in cancer and developmental disorders called RASopathies.[2]
There are many regulatory mechanisms that serve as a lock on this RAS-MAPK pathway, decreasing the likelihood of unintentional pathway activation. One is a protein dimer called 14-3-3 that keeps inactive RAF localized to the cytoplasm. An N-terminal phosphorylated serine keeps RAF bound to this protein dimer, and when the SMP complex is assembled, the catalytic subunit, PP1C, removes the phosphate group from the serine, releasing RAF from the 14-3-3 dimer, and activating the RAS-MAPK cell proliferation pathway.
In all images and animations, SHOC2 will be shown as cyan blue, MRAS as lime, and PP1C as violet. Other important components involved in the function of the SMP complex include the 14-3-3 dimer and Raf, which will be shown in salmon and slate-blue, respectively.
Structure of Subunits
SHOC2
SHOC2 is essential for complex formation, however SHOC2 only undergoes a 6° when MRAS and PP1C bind.[1] SHOC2 is just the place where MRAS and PP1C come together. SHOC2 and PP1C first engage in binding with each other, and MRAS-GTP binds, stabilizing SHOC2 and PP1C binding, and fully forming the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophophatase complex. [2]
PP1C
The protein phosphatase 1 catalytic (PP1C) subunit contains the catalytic site of the complex which dephosphorylates the N-terminal phosphoserine (NTpS) of RAF.[3] When PP1C is bound to the surface formed between SHOC2 and MRAS, the active site is exposed and fully accessible for the substrate to bind in the holoenzyme complex.[1] PP1C cannot act independently from the SMP complex because it lacks intrinsic substrate selectivity.[3] Therefore, PP1C requires the presence of SHOC2 and MRAS to function properly, whereas SHOC2 and MRAS may interact in a binary complex without the presence of PP1C.[1] SMP complex formation is initially mediated by SHOC2 and PP1C, then stabilized by the GTP interactions in MRAS and SHOC2.[2]
PP1C activity is regulated by PP1C-binding regulatory proteins.[1] The regulatory proteins may bind to small motifs in PP1C, like RVXF.[3] The RVXF motif is located in PP1C through the N-terminal disordered region.[2]
- FROM THE INITIAL FIRST DRAFT: SHOC2 has a RVxF binding motif that interacts with the PP1C RVxF binding site. The N-terminal loop of SHOC2 interacts with the RVxF binding site of PP1C, highlighting the structure and function connection of the complex. RVxF allows PP1C substrates to bind, whereas RAF has the RVxF motif, so it can bind to the hydrophobic region of SHOC2, allowing for greater specificity. Additionally, PP1C and SHOC2 do not change conformationally upon the binding of GTP, but rather they are inactive when RAS is bound to GDP due to steric strain. with or without binding to the SMP complex as PP1C retains its enzymatic function independently.[3].
MRAS
RAS proteins assist in signal transduction and are tightly regulated. MRAS, one of the subunits in the SMP complex, is a RAS protein specific to bind to SHOC2. Other RAS proteins may bind to SHOC2, but MRAS induces the complex formation with a significantly lower Kd (dissociation constant).[3] The formation of the SMP complex is stabilized and driven by the MRAS GTP-bound active state.[2][1] The tertiary structure formation is GTP dependent on multiple RAS forms.[1] When GTP is bound in MRAS, the SMP complex forms, but when GDP was bound to MRAS the SMP complex does not form.[3]
The SMP complex is localized to the cell membrane or other RAS isoforms by the C-terminus end of MRAS.[1]
In its , there is a modified chain that allows it to bind to the cell membrane.[3] Normally, MRAS does not have the chain and it is only added after the modification. For MRas to bind, the SHOC-2 complex must be in the GTP bound state. When GDP is bound, there is a steric clash between Switch 1 and PP1C, so interaction with MRAS is not possible. Additionally, the surface of MRAS that is buried in the complex overlaps the surfaces used to engage RAF. It requires two MRAS interactions to activate a single RAF molecule.
Autoinhibited Confirmation
The Ras-Raf signaling cascade will be inhibited without the dephosphorylation of Raf at Ser259. There is a dimer present in the cytoplasm that interacts with Raf through hydrogen bonds between R129 of 14-3-3 and Ser259 of Raf when Ser259 is phosphorylated. This interaction causes an as 14-3-3 restricts Raf to the cytoplasm and sterically inhibits Raf from binding with activated Ras. This interaction is crucial in regulating cell proliferation, as it prevents cell growth in the absence of a signal. Extracellular growth factors trigger GTP to bind to MRAS, which triggers SMP formation. Upon SMP complex formation, PP1C is brought into close proximity of Ras, leading to the dephosphorylation of Ser259 of Raf by the active site of PP1C. Once dephosphorylated, Raf is in the , allowing for the interaction of Ras and Raf, and the initiation of the signaling cascade.[4]
Signaling Cascade and Conformational Changes
Switch I and Switch II
SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is a regulator of a cell proliferation pathway. Mutations in cell proliferation pathways are responsible for 25% of all cancers 1. If this cell proliferation pathway goes unmediated, rapid cell growth and division will occur; the leading cause of cancers is mutations in this pathway. [5] Mechanistic Overview and Signaling Cascade shows the pathway SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is part of. It is a receptor tyrosine kinase pathway.[2] When MRAS is bound to GDP, the complex is not assembled. SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS all exist as separate monomers. The Raf domain contains a kinase domain (KD), Ras binding domain (RBD), a C-terminal phosphoserine (CTpS), a N-terminal phosphorylated serine (NTpS), and a 14-3-3 protein dimer, restricting RAF to the cytoplasm. In the activated pathway, MRAS is bound to GTP, and the SMP complex is assembled. PP1C is now in contact with the NTpS, allowing it to become dephosphorylated. [5] This dephosphorylation causes the dimerization of two Raf proteins via their kinase domains as well as a conformational change. This conformation change causes the phosphorylation of other residues. Eventually, this leads to the unbinding of GDP from MRAS and the binding of GTP to MRAS, causing a shift from the to The Switch I region is made up of residues 42-48 of the MRAS domain.[2] These residues are crucial for the binding of MRAS, SHOC2, and PP1C. When GDP is bound to the MRAS domain, it is in the Since the gamma P is not bound to GDP, there are no hydrogen bond interactions with the oxygens of the phosphate group- hence the open conformation. When GTP is bound to MRAS, it is in the The closed conformation allows for the binding of SHOC2 and PP1C. The open conformation of MRAS sterically clashes with the binding site of SHOC2, which is why the complex is not assembled when GDP is bound. [2].
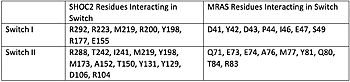
Figure 1. Residues Interacting at SWI and SWII at subunits SHOC2 and PP1C.
[3].
Switch I (SWI) and Switch II (SWII) are located between the SHOC2 and MRas subunits. When GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP, Switch I and Switch II relax, in the relaxed state SHOC2 cannot bind to MRas. Two Residues from MRas interact with the gamma phosphate on GTP, changing the complex to the closed confirmation. When GTP is bound to , it triggers the assembly of the SHOC2 Complex. When SWI is in its open confirmation, PP1C cannot bind with MRas due to the steric clashes, but when GTP binds and SWI is in its closed confirmation, PP1C can bind without hinderance. In a mutated complex, other RAS proteins can replace MRas making cell proliferation more likely. SHOC2-PP1C-MRas may be used as a therapeutic target for cancer treatments through changing the confirmation of the .
Ras/Raf
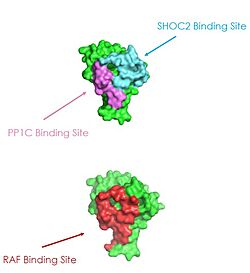
Figure 2: MRAS binding sites with SHOC2, PP1C, and RAF (PDB 7DSO).
[3].
Ras proteins are GTP-dependent intracellular switches that are anchored to the plasma membrane. Ras proteins activate RAF kinases through direct binding and membrane recruitment, resulting in RAF dimerization and pathway activation. [3]. Ras has a hydrophobic fatty acid tail, keeping it anchored to the membrane. There are no known membrane interacting regions on SHOC2 and PP1C, meaning MRAS likely recruits them to the membrane. Significant amount of steric overlap is seen in MRAS for the binding sites of PP1C, SHOC2, and Raf. MRAS is shown in green, with the SHOC2 binding site colored cyan, the PP1C binding site colored green, and the RAF binding site shown in red on a different RAS protein. Hence, multiple Ras proteins are required for further activation of the receptor tyrosine kinase pathway. Due to the significant overlap in binding domains, one Ras molecule is needed to recruit SHOC2 and PP1C to the membrane, and one Ras molecule is needed activate Raf. The ability of Ras-GTP to cluster at the membrane is a crucial capability for this protein complex. This anchoring is possible due to the presence of a hydrophobic fatty acid tail on Ras. The presence of this palmitoyl tail on Raf also localizes the complex to the cell membrane, allowing only for 2D movement and increasing local concentrations of the players needed in this signaling pathway.
Structure of Active Site
3-Metal Ion Catalysis
The of the SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS complex resides in the PP1C subunit.[6] The role of PP1C is to dephosphorylate SER259 of Raf so that the signaling cascade can start. The active site is unchanged upon the binding of the complex, however, SHOC2 and MRAS aid in the specificity of the enzymatic activity as PP1C is able to dephosphorylate many different targets on its own, with almost 100 PP1C targets found.[4] The full mechanism for the catalytic activity is unknown, however, there are 3 metal ions present (2-Mg2+ and 1-Cl-) to stabilize the waters present in the active site. Additionally, the substrate binds through hydrogen bonds with the main chain and side chain atoms of the catalytic residues. Mutations in the active site lead to increased activity, causing the Ras/Raf signaling cascade to be triggered more frequently.[6]
Hydrophobic Binding Site
PP1C has a
adjacent to its active site.[6] The majority of PP1C targets are able to bind through a specific motif that is recognized by the hydrophobic groove. In the Ras/Raf signaling cascade, the region of Raf that is C-terminal to the phosphate group binds to the hydrophobic groove, and the remaining residues bind to the hydrophobic region of SHOC2. This binding to SHOC2 is what allows the SMP complex to be more specific than PP1C on its own.[6] PP1C also has a singular cysteine (C291) present in the hydrophobic binding site in order to provide further stability to the substrate-protein interaction.
Significance
Cell Proliferation
The Ras-Raf signaling cascade is fundamental for cell growth and survival. Ras is a membrane-bound monomeric GTPase that, when activated by extracellular growth proteins, an inactive GDP is exchanged for a GTP molecule which activates Ras and starts the signaling cascade. When GDP is bound to Ras, it is in the closed confirmation and does not interact with Raf or other proteins. When MRAS is GTP-bound, it triggers the formation of the SMP complex. The active site of PP1C, when in complex, is responsible for removing the phosphate group from Ser259 of Raf that causes steric clash, and therefore, preventing auto-inhibition and releasing Raf. Extracellular growth factors initially trigger formation of the SMP complex which, after activation of Raf, allows for the interaction of Ras and Raf through a second Ras protein. This interaction triggers the Ras-Raf signaling cascade, which is what ultimately leads to cell proliferation. SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS plays a crucial gatekeeping role in the activation of the signaling cascade, making it a main regulation point of cell proliferation.
Cancer and Rasopathies
Mutations in any of the 3 subunits of SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS can lead to cancer or a family of developmental disability called Rasopathies. Mutations can occur at any of the SMP interfaces, leading to increased interaction energy and stability.[2] For SHOC2 and PP1C, common mutations lead to amino acid changes on the interaction surfaces, causing a higher affinity for binding.[5] Mutations to MRAS lead to consistent GTP-loading, causing an increase in the formation of the SMP complex and there is consistent activation of the cell-proliferation pathway in the absence of external growth factors. Common mutations in PP1C lead to increased active site activity, causing an increase in the Raf proteins that are active and available to bind to Ras. When the system is unregulated, cells proliferate regardless of external signals, leading to cancer and/or RASopathies.
Future Directions
The depletion of SHOC2 is being studied as a target for cancer and Rasopathy treatment.[2] Although MRAS is the protein that triggers the formation of the complex, SHOC2 is the anchoring location for both MRAS and PP1C. Without SHOC2, the complex would not form and Ser259 would not be dephosphorylated. MRAS could be triggered and moved towards the cell membrane, but no complex will form and Raf will remain in the auto-inhibited form. Additionally, there are other RAS proteins that can form an SMP-like complex. If MRAS were to be depleted, other RAS proteins could step in place of MRAS. PP1C is able to dephosphorylated other proteins on it's own, therefore it is not a good target as depletion of PP1C could lead to other issues. Depletion of SHOC2 is the most promising treatment that has been researched. There is also possibility that changing the confirmation of RAS Switch II could lead to decreased cell proliferation.


