We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1767
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
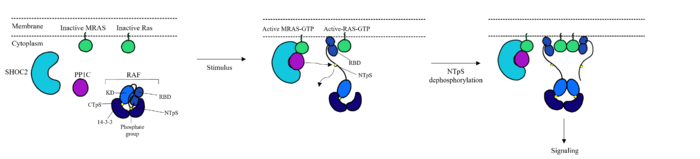
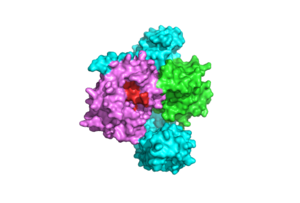
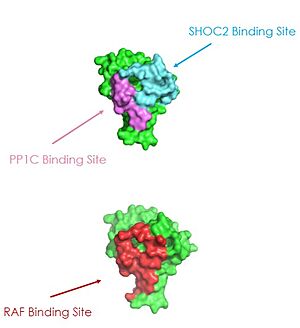
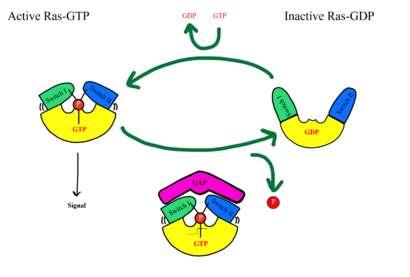
| - | <scene name='95/ | + | <scene name='95/952695/Overall_image/1'>The SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C</scene> (SMP) holophosphatase complex functions as a key regulator of the [https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/rtk-14050230/#:~:text=One%20of%20the%20most%20common,anchored%20to%20the%20plasma%20membrane. receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)] signaling pathway by removing an inhibitory phosphate on the [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167488907001164. RAF] family of proteins to allow for [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3536342/. MAPK signaling].<ref name="Kwon">PMID: 35831509</ref> This interaction of the RTK-RAS pathway and the SMP complex drives cell proliferation.<ref name="Hauseman">PMID:35830882</ref> The SMP complex is made of three subunits, SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. Each of these subunits has a different shape that corresponds to its different function. <scene name='95/952695/Shoc2intro/1'>The SHOC2 subunit</scene> uses a crescent shape to enhance substrate interactions and complex stability.<ref name="Liau">PMID: 35768504</ref> <scene name='95/952695/Pp1cintro/3'>The PP1C subunit</scene> contains the the catalytic site of the complex which dephosphorylates the N-terminal phosphoserine (NTpS) of RAF green link here.<ref name="Liau">PMID: 35768504</ref> <scene name='95/952694/Pp1ccorrectintro/1'>The MRAS subunit</scene> binds to GTP which causes assembly of the SMP complex. The <scene name='95/952695/413cellmemprotrusion/4'>C-terminus of MRAS</scene> localizes the complex to the cell membrane.<ref name="Liau">PMID: 35768504</ref> Once the SMP compelx is assembled, MRAS can bind to <scene name='95/952695/Raf/2'>RAF</scene>, allowing the [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5000522/. signaling cascade] to continue. Mutations in one or multiple of these subunits leads to over-activation of the signaling pathway, which may result in cancer and developmental disorders called [https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/rasopathies.html RASopathies].<ref name="Kwon">PMID: 35831509</ref> |
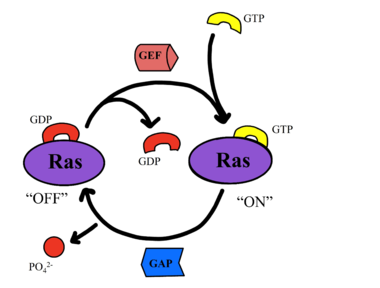
There are many regulatory mechanisms that serve as a lock on this [https://www.cancer.gov/research/key-initiatives/ras/about#:~:text=RAS%20proteins%20are%20important%20for,inactive%20(GDP%20form)%20states. RAS]-[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3536342/. MAPK] pathway, decreasing the likelihood of unintentional pathway activation. <ref name="Hauseman">PMID:35830882</ref> One example is <scene name='95/952695/14-3-3/1'>14-3-3</scene>, a protein dimer that keeps inactive RAF localized to the cytoplasm. An N-terminal phosphorylated serine (NTpS) keeps RAF bound to this protein dimer, and when the SMP complex is assembled, the catalytic subunit, PP1C, removes the phosphate group from the serine residue, releasing RAF from <scene name='95/952695/14-3-3/1'>14-3-3</scene>, and activating the RAS-MAPK cell proliferation pathway. <ref name="Hauseman">PMID:35830882</ref> | There are many regulatory mechanisms that serve as a lock on this [https://www.cancer.gov/research/key-initiatives/ras/about#:~:text=RAS%20proteins%20are%20important%20for,inactive%20(GDP%20form)%20states. RAS]-[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3536342/. MAPK] pathway, decreasing the likelihood of unintentional pathway activation. <ref name="Hauseman">PMID:35830882</ref> One example is <scene name='95/952695/14-3-3/1'>14-3-3</scene>, a protein dimer that keeps inactive RAF localized to the cytoplasm. An N-terminal phosphorylated serine (NTpS) keeps RAF bound to this protein dimer, and when the SMP complex is assembled, the catalytic subunit, PP1C, removes the phosphate group from the serine residue, releasing RAF from <scene name='95/952695/14-3-3/1'>14-3-3</scene>, and activating the RAS-MAPK cell proliferation pathway. <ref name="Hauseman">PMID:35830882</ref> | ||
Revision as of 03:35, 17 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Kwon JJ, Hajian B, Bian Y, Young LC, Amor AJ, Fuller JR, Fraley CV, Sykes AM, So J, Pan J, Baker L, Lee SJ, Wheeler DB, Mayhew DL, Persky NS, Yang X, Root DE, Barsotti AM, Stamford AW, Perry CK, Burgin A, McCormick F, Lemke CT, Hahn WC, Aguirre AJ. Structure-function analysis of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. PMID:35831509 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Hauseman ZJ, Fodor M, Dhembi A, Viscomi J, Egli D, Bleu M, Katz S, Park E, Jang DM, Porter KA, Meili F, Guo H, Kerr G, Molle S, Velez-Vega C, Beyer KS, Galli GG, Maira SM, Stams T, Clark K, Eck MJ, Tordella L, Thoma CR, King DA. Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. PMID:35830882 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 3.17 3.18 3.19 3.20 3.21 3.22 3.23 Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Jun 29. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. PMID:35768504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 Lavoie H, Therrien M. Structural keys unlock RAS-MAPK cellular signalling pathway. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):248-249. PMID:35970881 doi:10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Young LC, Hartig N, Boned Del Río I, Sari S, Ringham-Terry B, Wainwright JR, Jones GG, McCormick F, Rodriguez-Viciana P. SHOC2-MRAS-PP1 complex positively regulates RAF activity and contributes to Noonan syndrome pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10576-E10585. PMID:30348783 doi:10.1073/pnas.1720352115
- ↑ Kelker MS, Page R, Peti W. Crystal structures of protein phosphatase-1 bound to nodularin-R and tautomycin: a novel scaffold for structure-based drug design of serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitors. J Mol Biol. 2009 Jan 9;385(1):11-21. Epub 2008 Nov 1. PMID:18992256 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.053
Student Contributors
- Sloan August
- Rosa Trippel
- Kayla Wilhoite