User:Eduardo Soares/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
Notably, the PilZ protein in Pseudomonas aeruginosa contains a single 118-residue domain exhibiting substantial sequence similarity to the C-terminus of BcsA. Within the pil operon, responsible for the synthesis and functionality of pili, PilZ is among the few proteins with an unknown function. This operon plays a role in the transition from motile to sessile growth modes, although the precise regulatory mechanisms remain elusive. Strains lacking the PilZ domain (ΔpilZ) can produce normal levels of pilin protomers but are unable to assemble functional pili. | Notably, the PilZ protein in Pseudomonas aeruginosa contains a single 118-residue domain exhibiting substantial sequence similarity to the C-terminus of BcsA. Within the pil operon, responsible for the synthesis and functionality of pili, PilZ is among the few proteins with an unknown function. This operon plays a role in the transition from motile to sessile growth modes, although the precise regulatory mechanisms remain elusive. Strains lacking the PilZ domain (ΔpilZ) can produce normal levels of pilin protomers but are unable to assemble functional pili. | ||
Furthermore, other PilZ-domain proteins have been implicated in the regulation of motility across various organisms. For instance, the YcgR protein in Escherichia coli and the DgrA and DgrB proteins in Caulobacter crescentus have demonstrated involvement in controlling motility under high cytosolic c-di-GMP concentrations. Notably, certain PilZ domains are situated at the C-terminus of proteins participating in processes sensitive to c-di-GMP levels. Alg44 from P. aeruginosa represents another example, functioning as an essential protein in the c-di-GMP-regulated process of alginate biosynthesis. These discoveries provide robust evidence supporting the hypothesis that the majority of PilZ domains function as effectors, binding c-di-GMP, and exerting a critical role in the regulation of various cellular processes. | Furthermore, other PilZ-domain proteins have been implicated in the regulation of motility across various organisms. For instance, the YcgR protein in Escherichia coli and the DgrA and DgrB proteins in Caulobacter crescentus have demonstrated involvement in controlling motility under high cytosolic c-di-GMP concentrations. Notably, certain PilZ domains are situated at the C-terminus of proteins participating in processes sensitive to c-di-GMP levels. Alg44 from P. aeruginosa represents another example, functioning as an essential protein in the c-di-GMP-regulated process of alginate biosynthesis. These discoveries provide robust evidence supporting the hypothesis that the majority of PilZ domains function as effectors, binding c-di-GMP, and exerting a critical role in the regulation of various cellular processes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==c-di-GMP== | ||
==Molecular Interaction== | ==Molecular Interaction== | ||
Revision as of 12:54, 23 June 2023
VCA0042/plzD complexed with c-di-GMP
Introduction
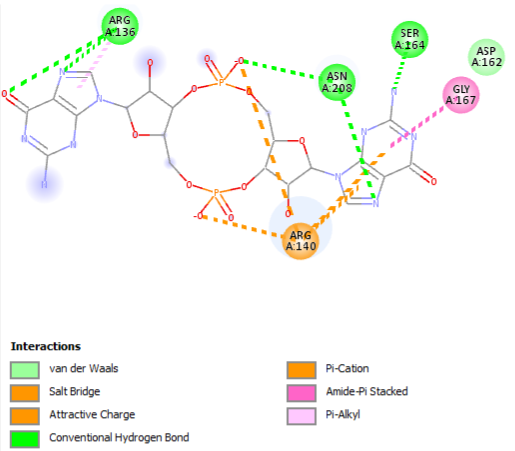
The PDB code 2RDE represents a PilZ protein complexed with cyclic diguanylate monophosphate (c-di-GMP) in Vibrio cholera there is a molecular interaction involved in the regulation of bacterial biofilm formation and motility. The complex is formed by the binding of the small signaling molecule c-di-GMP to a protein domain known as PilZ. This interaction plays a crucial role in bacterial physiology and is implicated in various cellular processes.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Benach J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.