User:Matheus Andrade Bettiol/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
This protein is an important molecular switch for activities associated with the cytoskeleton and the immune system. In relation to the cytoskeleton, it is a regulator or the cell migration, contributing to cell retraction through the ROCK ([[Rho-associated protein kinase]]) and LIMK (LIM kinase) pathway, which leads to contraction of acto-myosin II and [[actin]] polymerization. In addition, it is relevant for the assembly of occlusive junctions that seal the epithelium in selective permeability barriers, such as in the intestine. When it comes to the immune system, it is essential for the presentation of antigens and formation of immune synapses between the dendritic cell and the T lymphocyte. Not only that, but it also contributes to the recruitment and phagocytosis activity of neutrophils, macrophages and dendritic cells. | This protein is an important molecular switch for activities associated with the cytoskeleton and the immune system. In relation to the cytoskeleton, it is a regulator or the cell migration, contributing to cell retraction through the ROCK ([[Rho-associated protein kinase]]) and LIMK (LIM kinase) pathway, which leads to contraction of acto-myosin II and [[actin]] polymerization. In addition, it is relevant for the assembly of occlusive junctions that seal the epithelium in selective permeability barriers, such as in the intestine. When it comes to the immune system, it is essential for the presentation of antigens and formation of immune synapses between the dendritic cell and the T lymphocyte. Not only that, but it also contributes to the recruitment and phagocytosis activity of neutrophils, macrophages and dendritic cells. | ||
| + | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 44: | Line 45: | ||
C-terminal Prenylation Site: The C-terminal region of RhoA undergoes prenylation, a post-translational modification where a prenyl lipid group (such as farnesyl or geranylgeranyl) is attached. Prenylation allows RhoA to anchor to cell membranes, facilitating its localization and interaction with membrane-associated proteins. | C-terminal Prenylation Site: The C-terminal region of RhoA undergoes prenylation, a post-translational modification where a prenyl lipid group (such as farnesyl or geranylgeranyl) is attached. Prenylation allows RhoA to anchor to cell membranes, facilitating its localization and interaction with membrane-associated proteins. | ||
| + | |||
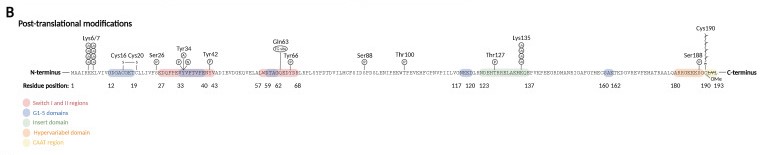
== Post-Translational Modifications == | == Post-Translational Modifications == | ||
| - | Prenylation: the activation of Rho | + | Prenylation: the activation of [[Rho GTPase]] require membrane binding, which is necessary for the interaction with membranous GEFs. The membrane association requires C-terminal prenylation, which involves the addition of a geranylgeranyl (20-carbon chain) to Cys190 in the CAAX motif. |
Phosphorylation: can alter the subcellular localization of RhoA when occurs close to C-terminal lipid modifications. On the other hand, phosphorylation of the G-domain affects GTP/GDP cycling and the interaction with effector proteins. | Phosphorylation: can alter the subcellular localization of RhoA when occurs close to C-terminal lipid modifications. On the other hand, phosphorylation of the G-domain affects GTP/GDP cycling and the interaction with effector proteins. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 57: | ||
Adenylation: adenylation on Tyr34 (switch I region) leads to RhoA inhibition. | Adenylation: adenylation on Tyr34 (switch I region) leads to RhoA inhibition. | ||
| - | Ubiquitination: target the protein for degradation by the proteasome. RhoA is ubiquitylated by E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes, that ubiquitinate either active RhoA on Lys6 and Lys7, inactive RhoA, or both states on Lys135. | + | Ubiquitination: target the protein for degradation by the proteasome. RhoA is ubiquitylated by E3 [[ubiquitin protein ligase]] complexes, that ubiquitinate either active RhoA on Lys6 and Lys7, inactive RhoA, or both states on Lys135. |
[[Image:Pos-translational_modifications_RhoA.jpg]] | [[Image:Pos-translational_modifications_RhoA.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 21:26, 25 June 2023
==rhoA==
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644