User:Matheus Andrade Bettiol/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
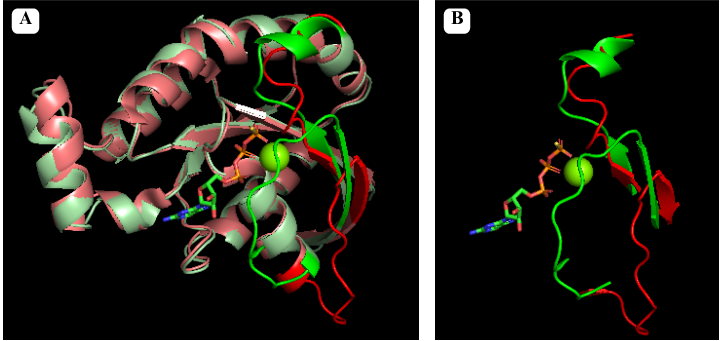
name='97/973102/Switch1_and_2_gdp/1'>RhoA-GDP</scene>. Their conformations dictate the ability of RhoA to interact with downstream effector proteins. | name='97/973102/Switch1_and_2_gdp/1'>RhoA-GDP</scene>. Their conformations dictate the ability of RhoA to interact with downstream effector proteins. | ||
<scene name='97/973102/Insertion_region/2'>Rho Insert</scene>: This is a unique sequence insertion found within the GTPase domain of RhoA. It plays a role in the regulation and interaction of RhoA with other proteins. | <scene name='97/973102/Insertion_region/2'>Rho Insert</scene>: This is a unique sequence insertion found within the GTPase domain of RhoA. It plays a role in the regulation and interaction of RhoA with other proteins. | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='97/973102/C-terminal/1'>Hypervariable C-terminal</scene>: <span style="color:orange;background-color:white;font-weight:bold;">The C-terminal region (in orange)</span> of RhoA undergoes prenylation, a post-translational modification where a prenyl lipid group (such as farnesyl or geranylgeranyl) is attached. Prenylation allows RhoA to anchor to cell membranes, facilitating its localization and interaction with membrane-associated proteins. | ||
[[Image:A.png]] | [[Image:A.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='97/973102/C-terminal/1'>Hypervariable C-terminal</scene>: <span style="color:orange;background-color:white;font-weight:bold;">The C-terminal region (in orange)</span> of RhoA undergoes prenylation, a post-translational modification where a prenyl lipid group (such as farnesyl or geranylgeranyl) is attached. Prenylation allows RhoA to anchor to cell membranes, facilitating its localization and interaction with membrane-associated proteins. | ||
== Post-Translational Modifications == | == Post-Translational Modifications == | ||
Revision as of 20:03, 14 July 2023
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Jaffe AB, Hall A. Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:247-69. PMID:16212495 doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.020604.150721
- ↑ Bros M, Haas K, Moll L, Grabbe S. RhoA as a Key Regulator of Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Cells. 2019 Jul 17;8(7):733. PMID:31319592 doi:10.3390/cells8070733
- ↑ Hetmanski JH, Zindy E, Schwartz JM, Caswell PT. A MAPK-Driven Feedback Loop Suppresses Rac Activity to Promote RhoA-Driven Cancer Cell Invasion. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 May 3;12(5):e1004909. PMID:27138333 doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004909
- ↑ Schmidt SI, Blaabjerg M, Freude K, Meyer M. RhoA Signaling in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells. 2022 May 1;11(9):1520. PMID:35563826 doi:10.3390/cells11091520
- ↑ Xu H, Yang J, Gao W, Li L, Li P, Zhang L, Gong YN, Peng X, Xi JJ, Chen S, Wang F, Shao F. Innate immune sensing of bacterial modifications of Rho GTPases by the Pyrin inflammasome. Nature. 2014 Sep 11;513(7517):237-41. doi: 10.1038/nature13449. Epub 2014 Jun 11. PMID:24919149 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13449
- ↑ Ihara K, Muraguchi S, Kato M, Shimizu T, Shirakawa M, Kuroda S, Kaibuchi K, Hakoshima T. Crystal structure of human RhoA in a dominantly active form complexed with a GTP analogue. J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 17;273(16):9656-66. PMID:9545299
- ↑ Shimizu T, Ihara K, Maesaki R, Kuroda S, Kaibuchi K, Hakoshima T. An open conformation of switch I revealed by the crystal structure of a Mg2+-free form of RHOA complexed with GDP. Implications for the GDP/GTP exchange mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 16;275(24):18311-7. PMID:10748207 doi:10.1074/jbc.M910274199
- ↑ Schmidt SI, Blaabjerg M, Freude K, Meyer M. RhoA Signaling in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells. 2022 May 1;11(9):1520. PMID:35563826 doi:10.3390/cells11091520