We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Preston Roa/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
=== Extracellular Domain === | === Extracellular Domain === | ||
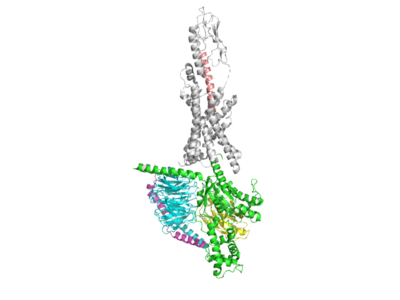
| - | Broadly the extracellular reactions between GLP-1 and GLP-1R lie between residues 15-32 on the peptide GLP-1. Residues L32, F28, W31 of the peptide and L36 and W214 of the receptor all utilize hydrophobic interactions or van der waals for affinity and binding, but exclusively F28, W31, and W214 have pi | + | Broadly the extracellular reactions between GLP-1 and GLP-1R lie between residues 15-32 on the peptide GLP-1. Residues L32, F28, W31 of the peptide and L36 and W214 of the receptor all utilize hydrophobic interactions or van der waals for affinity and binding, but exclusively F28, W31, and W214 have pi stacking which future maximizes interactions to increase binding. <scene name='10/1037514/Extracellular_interactions/4'>Pi Stacking and Hydrophobic Interactions</scene> Furthermore, there is a strong hydrogen bond between D15 of the peptide to the R380 receptor. <scene name='10/1037514/Extracellular_interactions_2/3'>Hydrogen Bond</scene> Van der Waals interactions continue on the residues Y19, L20, and V16 on the peptide as they interact with L141 and L210 of the receptor. Another hydrogen bond between E27 and Q21 also occurs. <scene name='10/1037514/Extracellular_interactions_3/3'>Hydrophobic Interactions and Hydrogen Bond</scene> Finally, there is a patch of extensive hydrogen bonding in an almost chainlike fashion goin from L32 of the receptor to E21 of the peptide, to R299 of the receptor, to the S17 of the peptide which then interacts with Y205 and T298 both of the receptor. <scene name='10/1037514/Extracellular_interactions_3/3'>Extensive Hydrogen Bonding</scene> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1037514/Extracellular_interactions_3/3'>Extensive Hydrogen Bonding</scene> | + | |
=== Active Site/Binding Site === | === Active Site/Binding Site === | ||
| - | The transmembrane core is key to the active site/binding site. One of the main interactions between GLP-1 and GLP-1R includes the hydrogen bond between H7 and Q234 as the N-terminus of the peptide is bound to the transmembrane domain of the receptor. This interaction provides the most stability within the structure. It is further enhanced by hydrophobic interactions between residues V16 and F12 of the peptide and L384 and L141 of the receptor. Notably there is a hydrogen bond T13 of the peptide and K197 of the receptor. | + | The transmembrane core is key to the active site/binding site. One of the main interactions between GLP-1 and GLP-1R includes the hydrogen bond between H7 and Q234 as the N-terminus of the peptide is bound to the transmembrane domain of the receptor. This interaction provides the most stability within the structure. <scene name='10/1037514/Histidine_7/7'>Histidine 7 Interaction</scene> It is further enhanced by hydrophobic interactions between residues V16 and F12 of the peptide and L384 and L141 of the receptor. Notably there is a hydrogen bond T13 of the peptide and K197 of the receptor. <scene name='10/1037514/Other_n-terminus_interactions/4'>Hydrophobic and Hydrogen Bonding in N-Terminus</scene> <scene name='10/1037513/Glp_bound_to_glp-1r_h_bonds/4'>GLP-1 bound to GLP-1R H-bonds</scene> <scene name='10/1037513/Glp_bound_to_glp-1r_no_clash/3'>GLP-1 bound to GLP-1R: interactions, no steric clash</scene> |
| - | + | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1037513/Glp_bound_to_glp-1r_h_bonds/4'>GLP-1 bound to GLP-1R H-bonds</scene> | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | <scene name='10/1037513/Glp_bound_to_glp-1r_no_clash/3'>GLP-1 bound to GLP-1R: interactions, no steric clash | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
=== Intracellular Domain === | === Intracellular Domain === | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 29 April 2024
GLP-1
| |||||||||||
References
[1] Drucker DJ, Habener JF, Holst JJ. Discovery, characterization, and clinical development of the glucagon-like peptides. J Clin Invest. 2017 Dec 1;127(12):4217-4227. doi: 10.1172/JCI97233. Epub 2017 Dec 1. PMID: 29202475; PMCID: PMC5707151.
[2] Mayendraraj, A., Rosenkilde, M. M., & Gasbjerg, L. S. (2022). GLP-1 and GIP receptor signaling in beta cells - A review of receptor interactions and co-stimulation. Peptides, 151, 170749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170749
[3] Seino, Y., Fukushima, M., & Yabe, D. (2010). GIP and GLP-1, the two incretin hormones: Similarities and differences. Journal of diabetes investigation, 1(1-2), 8–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00022.x
Student Contributors
- Preston Roa
- Jack Guckien
- Sam Reichenbach