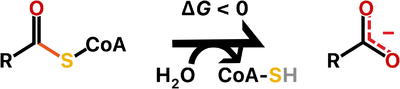Mitochondrial hotdog-fold thioesterase
From Proteopedia
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Structure and active site == | == Structure and active site == | ||
| - | '''Thioesterase''' superfamily members 4 (Them4) and 5 (Them5) are proteins found in | + | '''Thioesterase''' superfamily members 2 (Them2) 4 (Them4) and 5 (Them5) are proteins found in mammalian [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitochondrion mitochondria], but may also occur in other compartments such as the endoplasmic reticulum and the citosol. |
Our text is mainly focused on the crystal structure solved by [[X-ray crystallography]] at 2.3Å resolution of the complex between the recombinant Δ39Them4 protein and the inhibitor undecan-2-one-CoA. | Our text is mainly focused on the crystal structure solved by [[X-ray crystallography]] at 2.3Å resolution of the complex between the recombinant Δ39Them4 protein and the inhibitor undecan-2-one-CoA. | ||
To start a precise analysis of Them4, it is interesting to switch the space filling representation to the <scene name='10/1049462/Cartoon/2'>cartoon representation</scene>, which reveals the secondary structure elements that are present within this protein's folding. Furthermore, we shall start with a <scene name='10/1049462/Monomerb/3'>tertiary structure</scene>, represented here by the subunit B. | To start a precise analysis of Them4, it is interesting to switch the space filling representation to the <scene name='10/1049462/Cartoon/2'>cartoon representation</scene>, which reveals the secondary structure elements that are present within this protein's folding. Furthermore, we shall start with a <scene name='10/1049462/Monomerb/3'>tertiary structure</scene>, represented here by the subunit B. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Notwithstanding that hotdog-fold thioesterases are mainly grouped by their atomic structure since there is little similarity in their primary structure, it is notable that Them4 and Them5 possess a conserved <scene name='10/1049462/Hggdt/4'>HGG…D…T</scene> motif also observed in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_homology#Orthology orthologs]. | Notwithstanding that hotdog-fold thioesterases are mainly grouped by their atomic structure since there is little similarity in their primary structure, it is notable that Them4 and Them5 possess a conserved <scene name='10/1049462/Hggdt/4'>HGG…D…T</scene> motif also observed in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_homology#Orthology orthologs]. | ||
| - | In Them4, the catalytic residues are <scene name='10/1049462/Thr-asp/4'>Asp161 and Thr177</scene>, which <scene name='10/1049462/H-bond_activesite/1'>interact</scene> through a [[hydrogen bond]] between the carboxylate in aspartate and the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydroxy_group hydroxyl] in threonine. For Them5, the catalytic residues are Asp167 and Thr183. | + | In Them4, the catalytic residues are <scene name='10/1049462/Thr-asp/4'>Asp161 and Thr177</scene>, which <scene name='10/1049462/H-bond_activesite/1'>interact</scene> through a [[hydrogen bond]] between the carboxylate in aspartate and the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydroxy_group hydroxyl] in threonine. For Them5, the catalytic residues are Asp167 and Thr183 whereas for Them2, a smaller paralog, the catalytic residues are Asp65 and Ser83 (noticing that both threonine and serine are polar residues with a hydroxyl in the side chain). |
In the proposed [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_catalysis catalytic mechanism], the deprotonated aspartate residue abstracts a proton from a water molecule, making it very '''reactive''' and prone to a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophilic attack] on the thioester bond. | In the proposed [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme_catalysis catalytic mechanism], the deprotonated aspartate residue abstracts a proton from a water molecule, making it very '''reactive''' and prone to a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophilic attack] on the thioester bond. | ||
| - | As observed in other single hotdog-fold thioesterases, the [[biological assembly]] of Them4 and Them5 is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_dimer homodimer] with a '''2-fold symmetry axis'''. This <scene name='10/1049462/Dimer-hotdog/1'>dimer</scene> is maintained mainly by a '''network of hydrogen bonds''' between the residues from the <scene name='10/1049462/Strand6/5'>6th strand</scene> in each monomer. Notably, this network involves the backbone in strand 6 between the beta sheets as well as the side chain of <scene name='10/1049462/Strand6-atoms/2'>Asn179, Asn181 and Asn183</scene> from the same strand. As a result, the homodimer has a <scene name='10/1049462/Betasheet-dimer/2'>continuous antiparallel 12-stranded beta sheet</scene> around <scene name='10/1049462/Hotdog_dimer/1'>two central alpha helixes</scene> oriented antiparallel to one another. | + | As observed in other single hotdog-fold thioesterases, the [[biological assembly]] of, Them2, Them4 and Them5 is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_dimer homodimer] with a '''2-fold symmetry axis'''. This <scene name='10/1049462/Dimer-hotdog/1'>dimer</scene> is maintained mainly by a '''network of hydrogen bonds''' between the residues from the <scene name='10/1049462/Strand6/5'>6th strand</scene> in each monomer. Notably, this network involves the backbone in strand 6 between the beta sheets as well as the side chain of <scene name='10/1049462/Strand6-atoms/2'>Asn179, Asn181 and Asn183</scene> from the same strand. As a result, the homodimer has a <scene name='10/1049462/Betasheet-dimer/2'>continuous antiparallel 12-stranded beta sheet</scene> around <scene name='10/1049462/Hotdog_dimer/1'>two central alpha helixes</scene> oriented antiparallel to one another. |
| - | Additionally, there are other interactions that contribute in stabilizing the homodimer. As an example, there is a <scene name='10/1049462/Phe_cluster/2'>cluster of phenylalanine side chains</scene> - involving Phe111, Phe115 and Phe121 from both subunits - in another interface region which is stabilized by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrophobic_effect#Folding_of_macromolecules hydrophobic effect]. | + | Additionally, there are other interactions that contribute in stabilizing the homodimer. As an example from Them4, there is a <scene name='10/1049462/Phe_cluster/2'>cluster of phenylalanine side chains</scene> - involving Phe111, Phe115 and Phe121 from both subunits - in another interface region which is stabilized by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrophobic_effect#Folding_of_macromolecules hydrophobic effect]. |
| - | In this quaternary structure, for Them4 the catalytic residues from one monomer are <scene name='10/1049462/Dimer-hotdog-hggdt/4'>in proximity</scene> to His152, Gly153 and Gly154 from the other monomer, which are proposed to accommodate the thioester substrate within the active site. For Them5, Asp167 and Thr183 from one monomer are close to His158, Gly159 and Gly160 from the other monomer. | + | In this quaternary structure, for Them4 the catalytic residues from one monomer are <scene name='10/1049462/Dimer-hotdog-hggdt/4'>in proximity</scene> to His152, Gly153 and Gly154 from the other monomer, which are proposed to accommodate the thioester substrate within the active site. For Them5, Asp167 and Thr183 from one monomer are close to His158, Gly159 and Gly160 from the other monomer. Meanwhile, for Them2, Asp65 and Ser83 are close to His56, Gly57 and Gly58. |
| - | As a direct consequence, in each catalytically competent Them4 and Them5 there are <scene name='10/1049462/Dimer-hotdog-activesites/2'>two active sites</scene> located in the interface between monomers of the obligatory homodimer. | + | Specifically for Them2, there is evidence from x-ray crystallography that this protein may also form a homotetramer through back-to-back association of two homodimers. |
| + | As a direct consequence, in each catalytically competent Them4 and Them5 there are <scene name='10/1049462/Dimer-hotdog-activesites/2'>two active sites</scene> located in the interface between monomers of the obligatory homodimer, whereas for Them2 there are four active sites. | ||
| - | Besides the core hotdog-fold, in both Them4 and Them5 there is <scene name='10/1049462/Add-alphahelix/2'>another alpha helix</scene> in each monomer. | + | Besides the core hotdog-fold, in both Them2, Them4 and Them5 there is <scene name='10/1049462/Add-alphahelix/2'>another alpha helix</scene> in each monomer. In Them4 and Them5, this element of [[secondary structure]] is tightly attached to the convex side of the curved beta sheet over <scene name='10/1049462/Alt-alpha-beta/2'>strands 1 and 2</scene> owing to the hydrophobic effect. More specifically, it is an <scene name='10/1049462/Alt-alpha-beta_amph/3'>amphiphilic alpha helix</scene> whose {{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}} residues are spatially <scene name='10/1049462/Alt-alpha-beta_amph/4'>collapsed</scene> over {{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}} residues in those strands of the core beta sheet whereas the {{Template:ColorKey_Polar}} residues interact with the bulk water. For Them4, this alpha helix is formed by residues 55 to 68, while for Them5 the respective residues are 64 to 79. |
Interestingly, at each of the <scene name='10/1049462/Add-alphahelix-pi-stacking/2'>flanking regions</scene> of the additional alpha helix, there is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stacking_(chemistry) pi-stacking] interaction. For Them4, Trp53 and Phe61 make this interaction at the N-terminal side of the alpha helix while Phe64 and Trp73 are the analogues at the C-terminal side. | Interestingly, at each of the <scene name='10/1049462/Add-alphahelix-pi-stacking/2'>flanking regions</scene> of the additional alpha helix, there is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stacking_(chemistry) pi-stacking] interaction. For Them4, Trp53 and Phe61 make this interaction at the N-terminal side of the alpha helix while Phe64 and Trp73 are the analogues at the C-terminal side. | ||
From the PDB 4GAH crystal structure, Zhao ''et al.'' (2012) noted that chain B was better defined, as exemplified by one more alpha helix from residues <scene name='10/1049462/83-94_inb/1'>83-94</scene>, whereas this same region was structurally disordered in chain A and could not be observed. | From the PDB 4GAH crystal structure, Zhao ''et al.'' (2012) noted that chain B was better defined, as exemplified by one more alpha helix from residues <scene name='10/1049462/83-94_inb/1'>83-94</scene>, whereas this same region was structurally disordered in chain A and could not be observed. | ||
| - | Them4 also has <scene name='10/1049462/Turnsandcoils/1'>turns and coils</scene>, which is also observed in Them5. | + | Them4 also has <scene name='10/1049462/Turnsandcoils/1'>turns and coils</scene>, which is also observed in Them5 and Them2. |
== Interaction with the substrate == | == Interaction with the substrate == | ||
Revision as of 19:36, 31 May 2024
Overview of thioesterases
Thioesterases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of thioester bonds, which are the linkage between a carbonyl and a sulfur atom.
The ATP-dependent formation of a thioester bond from a carboxylate and a thiol in biomolecules makes them more reactive and is particularly an important commitment step in lipid metabolism. Therefore, thioesterases counteract this activation by releasing upon hydrolysis a molecule with the more stable carboxylate group. For this reason, thioesterases are found at the end of some metabolic pathways but they also may act as regulators of flux. Besides lipid metabolism, thioester bonds also occur in biosynthetic pathways for polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide production, as well as in main metabolites of carbon metabolism such as acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA.
There are two main families of thioesterases which are distinguished by their folding, named the α/β-hydrolases and the hotdog-fold hydrolases. Notably, these two different families are evolutionarily distant, so the thioesterase activity is a shared feature owing to convergent evolution.
| |||||||||||
Function
From enzymatic activities in vitro, it was shown that Them4 (Zhao et al., 2009) and Them5 (Zhuravleva et al., 2012) have higher kcat/KM for acyl-CoA's with medium and long hydrocarbon chain, such as myristoyl-CoA (14:0), palmitoyl-CoA (16:0), oleoyl-CoA (18:1) and linoleoyl-CoA (18:2). According to Zhuravleva et al. (2012), linoleoyl-CoA (18:2) was a preferred substrate for Them5. From studies with Them5−/− mice, it was identified by mass spectrometry (MS) that loss of Them5 is related to an increase in the levels of monolysocardiolipin (MLCL), which is a metabolite upstream of the cardiolipin remodeling process in mitochondria. Furthermore, the lipidomics analysis by MS for Them5−/− mice also revealed a 2-fold decrease of free fatty acids, notably linoleic (18:2) and linolenic (18:3) acids. This is consistent with the in vitro assay for the recombinant ∆34Them5 which revealed higher kcat/KM for linoleoyl-CoA (18:2). Moreover, it is observed by two-dimensional electron microscopy (2D-EM) and subsequent 3D reconstruction that in hepatocytes from Them5−/− mice, mitochondria were more elongated and interconnected, with a 2-fold increase in volume. With these data, Zhuravleva et al. (2012) propose that Them5 might be a regulator of cardiolipin remodeling through modulation of the unsaturated acyl-CoA pool in mitochondria. This modulation in turn seems to affect mitochondrial morphology.
Zhao et al. (2012) observed that Them4 shows very weak binding affinity (Ki > 1 mM) for carboxylic acids generated after the thioester bond hydrolysis, suggesting that this enzyme is not regulated by product inhibition.
Them4 is also called Akt C-Terminal Modulator Protein (CTMP), owing to previous data suggesting that it interacts with the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt1 in an inferred mechanism of regulating apoptosis. However, this putative activity is not well defined yet. Through pull-down assays, Zhao et al. (2012) verified that Them4 and Akt1 form a stable complex and that Them4 inhibits Akt1 activity in vitro, but Akt1 does not inhibit Them4.
References
Swarbrick, C. M., Nanson, J. D., Patterson, E. I., & Forwood, J. K. (2020). Structure, function, and regulation of thioesterases. Progress in Lipid Research, 79, 101036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2020.101036
Caswell, B. T., de Carvalho, C. C., Nguyen, H., Roy, M., Nguyen, T., & Cantu, D. C. (2022). Thioesterase enzyme families: Functions, structures, and mechanisms. Protein Science, 31(3), 652-676. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.4263
Zhao, H., Martin, B. M., Bisoffi, M., & Dunaway-Mariano, D. (2009). The Akt C-terminal modulator protein is an acyl-CoA thioesterase of the Hotdog-Fold family. Biochemistry, 48(24), 5507-5509. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi900710w
Zhao, H., Lim, K., Choudry, A., Latham, J. A., Pathak, M. C., Dominguez, D., ... & Dunaway-Mariano, D. (2012). Correlation of structure and function in the human hotdog-fold enzyme hTHEM4. Biochemistry, 51(33), 6490-6492. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi300968n
Zhuravleva, E., Gut, H., Hynx, D., Marcellin, D., Bleck, C. K., Genoud, C., ... & Hemmings, B. A. (2012). Acyl coenzyme A thioesterase Them5/Acot15 is involved in cardiolipin remodeling and fatty liver development. Molecular and cellular biology, 32(14), 2685-2697. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00312-12
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Marcelo Mesa, Thabata Fernanda Oliveira, Eduardo Ferraro, Michal Harel