Function
Interferons were the first cytokines discovered and were identified by Isaacs and Lindenmann. These proteins were classified as interferons because they interfered with virus growth.[1] The initial experiments performed poorly characterized the interferons, and was based merely on bioactivity. Advances in scientific instrumentation and technique have allowed for greater understanding and visualization of not only the structure but also the mechanisms of the various types of inteferons.[2] The interferons were originally classified as leukocyte (interferon-α), fibroblast (interferon-β), and immune (interferon-γ), although today they are classified into types I (α, β, ε, κ, ω), II (γ), and III (λ).[1][2]
- Interferon-γ induces macrophage stimulation toward antimicrobial and antitumor pathways[3]
- Interferon-λ has dual role in innate immunity and in long-term immunomodulatory effects on T- and B-cells[4]
- Interferon-τ functions in ensuring pregnancy continuation in ovine and bovine conceptuses[5]
Type I
Type I interferons are homologous helical cytokines that effect a wide variety of cells pleiotropically. These effects range from antiviral activity to antibacterial, antiprozoal, immunodulatory, and cell growth regulatory functions. Without Type I interferons, the survival of the higher vertebrates would be impossible. Because of their strong antiviral and antiproliferative effects, these interferons are used in the treatment of numerous cancers, hepatitis C, and multiple sclerosis. See Multiple sclerosis.
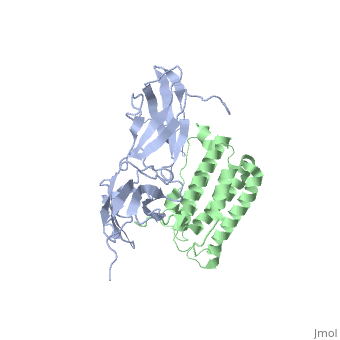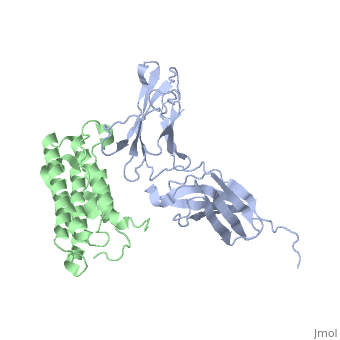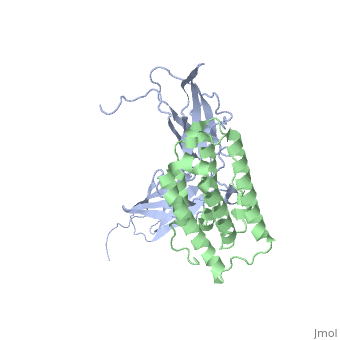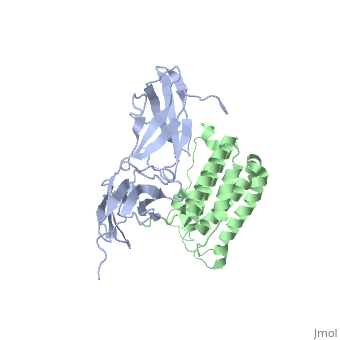
All type I interferons bind to a cell surface receptor consisting of two subunits: IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. These receptors belong to a class II helical cytokine receptor family (HCRII). Other members of this family include the interferon-γ receptor (IFNGR), tissue factor (TF), the interleukin 10 receptor (IL20R1 and IL20R2), IL-28BP, IFNLR, and IL28Rα.[6].
See more details in IntronA (Interferon alpha 2b)
Interferon-α
Interferon alpha has many with two : one between the , and the other between . It has seven and has several The helices A, C, and F run to one another, and to B, E, and G which run to each other.
does not run parallel or anti-parallel to either set, but rather runs at a 45-90 degree angle to them. Helix A consists of residues 10-12; Helix B of 40-43; Helix C of 53-68; Helix D of 70-75; Helix E of 78-100; Helix F of 109-132; and Helix G of 137-158.
Interferon-β
A protein growth factor that stimulates an antiviral defense is one of the only two known vertebrate structural genes that lacks introns.[7] Interferon-β has a 31% sequence homology to interferon-α . It is a relatively simple biological response modifier, with several . It consists of five , as compared to the seven of interferon-α, as well as multiple interconnecting . Helices A, B and D run , and helices C and E run to the other three helices, but to one another. Helix A consists of residues 6-23; Helix B consists of residues 49-65; Helix C consists of residues 77-91; Helix D consists of residues 112-131; and Helix E consists of residues 135-155.[8][9].
Interferon-β is used as a treatment for Multiple sclerosis, an autoimmune disease defined by Nylander and Hafler as "a multifocal demyelinating disease with progressive neurodegeneration caused by an autoimmune response to self-antigens in a genetically susceptible individual."[10] Inflammation is the primary cause of damage in MS, and though the effects of the disease are well known and various treatments exist for the disease, the exact identity of an antigen or infectious agent that causes the initiation of a myriad of symptoms is unknown.[11]. For more details see User:Chengfeng Ren/IFN beta 1a.
Comparison of three interferons
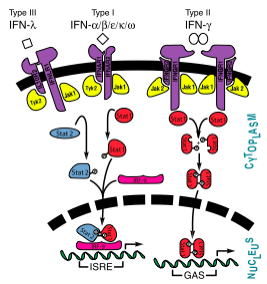
Interferon JAK-STAT Pathway showing interferons types I, II, and III
[1] Signaling and Receptor Interactions
The signaling pathways of interferons are interesting as type I interferons share the same receptors IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. Type II interferon-γ has receptors IFNGR1 and IFNGR2, but needs two interferon-γ to signal, as illustrated in the image to the right. Interestingly enough, types I and III act together in the JAK-STAT pathway, while type II acts alone. Interferon-α and -β bind to the same receptors as one another, the affinities with which they bind to IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 differ. While the binding to IFNAR2 is stronger for both in comparison to IFNAR1, interferon-β has a much stronger affinity for IFNAR1 than interferon-α.[12]
Interferon-α to an interferon receptor mainly with helices C and G. There are many within 4 angstroms of one another. These residues could form many , illustrated in white dotted lines. Given that interferon-α does not undergo many structural changes upon binding to interferon receptor II, Quadt-Akabayov et al. have concluded that the binding mechanism is similar to that of a lock and key. Interferons -α and -β interact with a receptor at the cell surface.[13] This receptor has : an
, with two disulfide bonds, a , with one disulfide bond, and a . The of the receptor have no secondary structure, allowing for some serious flexibility, leading to .[14]
Structural linkage between ligand discrimination and receptor activation by type I interferons [15]
Introduction
IFNs were the first cytokines discovered more than half a century ago as agents that interfere with viral infection. Since then, IFNs have been established as pleiotropic, multifunctional proteins in the early immune response, exhibiting pronounced antiproliferative effects on cells, in addition to their strong immunomodulatory and antiviral activities. Due to their potency and diverse biological activities, IFNs are used for the treatment of several human diseases, including hepatitis C, multiple sclerosis and certain types of cancer.
All initiate signaling by binding to the same cell surface receptor composed of two subunits called and . The intracellular domains (ICDs) of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 are associated with the Janus kinases (Jaks) Tyk2 and Jak1, respectively. Upon ligand binding by the IFNAR chains and formation of the signaling complex, these tyrosine kinases trans-phosphorylate and thereby activate each other. Subsequently, the activated Jaks phosphorylate STAT transcription factors, which translocate into the nucleus and activate the expression of hundreds of IFN-stimulated genes. To gain insight into how type I IFNs engage their receptor chains, how the receptor system is able to recognize the large number of different ligands, and how different IFN ligands can evoke different physiological activities, we determined the crystal structures of unliganded , the binary complex , and the ternary ligand-receptor complexes of and binding both receptor chains. A final theoretical ternary structure including was also created. These structures, in conjunction with biochemical and cellular experiments, reveal that the type I IFN receptor uses a mode of ligand interaction that is unique among cytokine receptors, but conserved between different IFNs. Furthermore, ligand discrimination occurs through distinct energetics of shared receptor contacts, and differential IFN signaling is mediated by specific ligand-receptor interface chemistries that lead to different ternary complex stabilities.
Interactions Between IFNAR & IFN
A superposition of the two ternary complexes reveals that they have very similar overall architectures, despite the different physiological activities of the IFN ligands. This suggests that the activity differences are not due to different signaling complex architectures. The functional differences are rather mediated by specific interface chemistries that form the basis for different ternary complex stabilities.
IFNAR2-IFN interaction
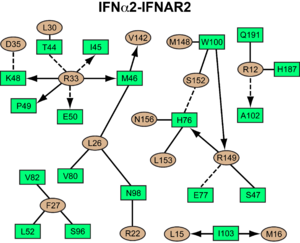
interacts primarily with the . Arg33(IFN) appears to be the for the interaction of the IFN ligand with IFNAR2. It forms an extensive hydrogen-bonding network with the main chain carbonyl oxygen atoms of Ile45(IFNAR2) and Glu50(IFNAR2) and the side chain of Thr44(IFNAR2). This residue is present in IFNa, IFNw, IFNb and IFNe. Two hydrophobic interaction clusters are part of the IFNa-IFNAR2 interface: the first one is formed between Leu15 and Met16 of the IFN molecule and Trp100 and Ile103 of IFNAR2; the second one comprises Leu26, Phe27, Leu30 and Val142 of the ligand and Met46, Leu52, Val80 and the methyl group of Thr44 of the receptor. Replacing reduces affinity by three orders of magnitude (the second most important residue for binding). This is surprising, as it is not engaged in any intimate contacts with IFNAR2 residues. One reason for its importance might be a .
Most of the residues involved in the IFNa2-IFNAR2 interaction are also found in the IFNw-IFNAR2 interface of the IFNw ternary complex.

A significant difference in the IFNAR2 interface between and IFNw is related to , which is replaced with Lys152 in . In the , this residue forms an with Glu149(IFN), but .
IFNAR1-IFN interaction
Because of the lower resolution of the IFNa ternary complex, we focused on the in our analysis of the IFN-IFNAR1 interface. In the , the only contains two hotspot residues we could experimentally confirm, and Phe238(IFNAR1). Substituting these residues by alanine reduces the affinity to all tested IFN ligands by more than 10-fold. On IFNw, mutation studies have shown that a charge-reversal mutation of Arg123 (Arg 120 on IFNa) leads to a total loss of activity.

Indeed, this residue forms a salt bridge with Asp132(IFNAR1) in addition to a hydrogen bond with Ser182(IFNAR1). Substitution of glutamate for Arg123(IFN) would lead to electrostatic repulsion with Asp132(IFNAR1).
The low affinity of IFNAR1 for the ligand appears to be functionally relevant, as weak binding to IFNAR1 is conserved between all alpha IFNs. Three amino acid substitutions on IFNa2 at positions His57, Glu58 and Ser61 to alanine or to Tyr, Asn, and Ser, respectively, confer tighter binding to IFNAR1, but leave the affinity to IFNAR2 essentially unaltered.
Implications for the binding mode of IFNb
30% and 33% sequence identity with and IFNa2, respectively. in our ternary complex structure leads of side chains (Tyr92 and ) with the receptors, indicating that the IFNb ligand could be easily accommodated by the receptors in a position similar to IFNw and IFNa2. Furthermore, the shows that . As a result, Ala19(IFN), when mutated to tryptophan, promotes an increased binding affinity to IFNAR2, which is a result of the (as shown by double mutant cycle analysis).
Structural Movements
Structural pertubations upon binding
One of the more controversial aspects of cytokine signaling is whether receptor binding is sufficient to generate activity, or if it has to be accompanied by structural perturbations. The type I interferon signaling complex is a rare example of a cytokine receptor complex were the structures of all the components making up the biologically active complex were determined to high resolution in both their free and bound forms. of the unbound NMR structure with the ternary complex structure of interferon shows a small expansion during complex formation.
Both IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, however, undergo significant domain movements upon binding. Using the D1 domain as anchor, a of IFNAR2 upon binding, on a scale of 6-12 Å, is observed (comparison of the unbound receptor (1n6u) with the binary IFNa2-IFNAR2 complex). The superimposition of the IFNa2-IFNAR2 binary complex with IFN-IFNAR2 in the ternary complexes of 6-9 Å, and even between the ternary IFNa and IFNw complexes a movement of 3-5 Å is observed. The D2 domain is engaged in crystal contacts in all three structures, and it remains an open question if the conformational changes in IFNAR2 are physiologically relevant. Still, these movements could change the proximity or orientation of the ICDs and associated Jaks within the cell.
The low-affinity receptor chain, IFNAR1, also upon ligand binding. When using D1 as anchor, D3 is moving inwards (toward the ligand) by ~15 Å. This would generate an even larger movement of the membrane-proximal SD4 domain and the transmembrane helix. The conformational changes in IFNAR1 are necessary to form the full spectrum of interactions with the IFN ligand, and to form a stable signaling complex that is able to instigate downstream signaling. In contrast to SD3, SD4 seems to be highly flexible (even more than D2 of IFNAR2). One might suggest that the conformational changes in IFNAR1 by itself will be responsible for a reduced binding affinity of IFNAR1 and may slow down the rate of ligand association to IFNAR1 directly from solution.
See Also
3D Structures of interferon
Interferon 3D structures