Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
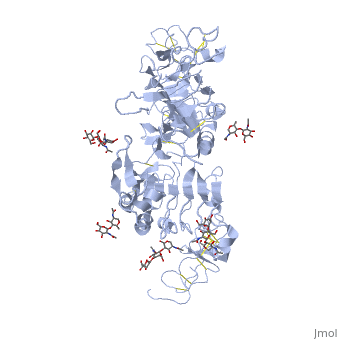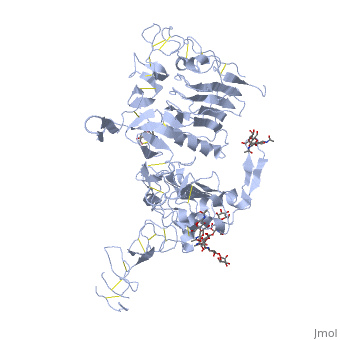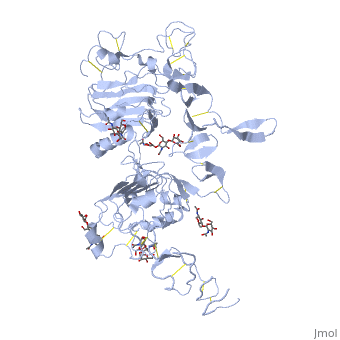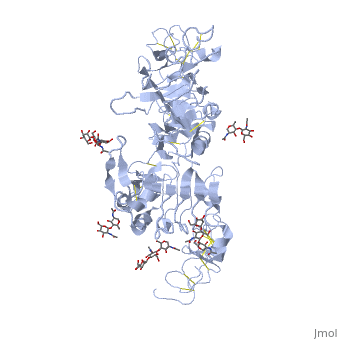
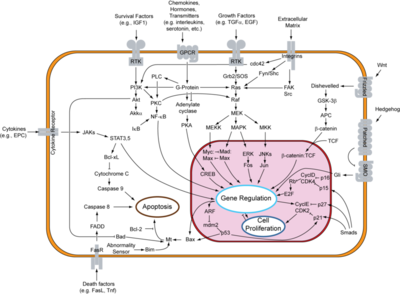
[[Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor]] (EGFR or '''ERBB1''') is found on the cell surface and associates to homodimers upon binding of its ligands such as the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) to its extracellular domain. The dimerization stimulates autophosphorylation of several tyrosine residues in the intracellular kinase domain which signal downstream transduction cascades. A human '''EGFR-2 (HER-2 or ERBB2)''' is involved in breast [[Cancer|cancer]] and is a major target for breast cancer [[Pharmaceutical Drugs|therapeutics]]. See more details in [[Herceptin - Mechanism of Action]]. '''ERBB3''' uses neuregulin as a ligand. '''ERBB4''' is a closely related [[Receptor tyrosine kinases|receptor tyrosine kinase]]. | [[Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor]] (EGFR or '''ERBB1''') is found on the cell surface and associates to homodimers upon binding of its ligands such as the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) to its extracellular domain. The dimerization stimulates autophosphorylation of several tyrosine residues in the intracellular kinase domain which signal downstream transduction cascades. A human '''EGFR-2 (HER-2 or ERBB2)''' is involved in breast [[Cancer|cancer]] and is a major target for breast cancer [[Pharmaceutical Drugs|therapeutics]]. See more details in [[Herceptin - Mechanism of Action]]. '''ERBB3''' uses neuregulin as a ligand. '''ERBB4''' is a closely related [[Receptor tyrosine kinases|receptor tyrosine kinase]]. | ||
| - | See also [[Kinase-linked, enzyme-linked and related receptors]] and [[EGFR | + | See also [[Kinase-linked, enzyme-linked and related receptors]] and [[EGFR Inhibitors]]. |
==Relevance== | ==Relevance== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Cancer
References
- ↑ D'Uva G, Aharonov A, Lauriola M, Kain D, Yahalom-Ronen Y, Carvalho S, Weisinger K, Bassat E, Rajchman D, Yifa O, Lysenko M, Konfino T, Hegesh J, Brenner O, Neeman M, Yarden Y, Leor J, Sarig R, Harvey RP, Tzahor E. ERBB2 triggers mammalian heart regeneration by promoting cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation and proliferation. Nat Cell Biol. 2015 May;17(5):627-38. doi: 10.1038/ncb3149. Epub 2015 Apr 6. PMID:25848746 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb3149
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sherrill JM, Kyte J. Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor by epidermal growth factor. Biochemistry. 1996 May 7;35(18):5705-18. doi: 10.1021/bi9602268. PMID:8639530 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi9602268
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Herbst RS. Review of epidermal growth factor receptor biology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59(2 Suppl):21-6. doi:, 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.11.041. PMID:15142631 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.11.041
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, Mardis E, Kupfer D, Wilson R, Kris M, Varmus H. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from "never smokers" and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 7;101(36):13306-11. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0405220101. Epub 2004 Aug 25. PMID:15329413 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405220101
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, David Canner, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky