Image:BRD Mechanism.jpg
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
Size of this preview: 800 × 130 pixels
Full resolution (2012 × 328 pixel, file size: 111 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
James Lignos (Talk | contribs)
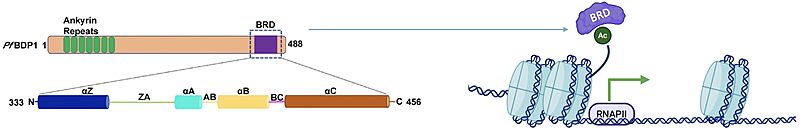
(Bromodomains are epigenetic "readers" that bind to acetylated lysines on N-terminal histone tails. Histone acetylation is a post translational modification that is associated with regions of chromatin that are primed for transcription. Bromodomains bind t)
Next diff →
Current revision
Bromodomains are epigenetic "readers" that bind to acetylated lysines on N-terminal histone tails. Histone acetylation is a post translational modification that is associated with regions of chromatin that are primed for transcription. Bromodomains bind to these modifications and recruit transcriptional machinery to promote gene expression.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | User | Dimensions | File size | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (current) | 14:27, 27 April 2025 | James Lignos (Talk | contribs) | 2012×328 | 111 KB | Bromodomains are epigenetic "readers" that bind to acetylated lysines on N-terminal histone tails. Histone acetylation is a post translational modification that is associated with regions of chromatin that are primed for transcription. Bromodomains bind t |
- Edit this file using an external application
See the setup instructions for more information.
Links
The following pages link to this file:
