Sand box 326
From Proteopedia
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== Sequence Analysis == | == Sequence Analysis == | ||
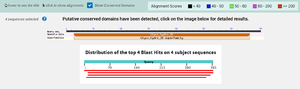
| - | + | According to BLAST, 3CBW has similar sequences to 2QHA (Beta-1,4-mannanase) and 2WHK (Mannan endo-1,4-beta-mannosidase). This means that 3CBW is in the mannanase super family. | |
| - | + | [[Image:BLAST.png |300px|center|thumb|]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Structural Analysis (DONE) == | == Structural Analysis (DONE) == | ||
Revision as of 01:45, 28 April 2025
3CBW Structure and Proposed Functionality
(NOTE TO ALL EDITORS: This page is part of a final project for a biochemistry lab at Elizabethtown College. Please do not edit this.)
3CBW is a homodimeric protein complex that originates from the bacterial species Chitinophaga Pinensis and has a mass of 80.65 kDa. It is a member of the SGNH Hydrolase Superfamily with structural and sequential similarities to esterases and lipases. Current evidence suggests it causes the hydrolysis of esters and/or acetyl groups on lipids/lipid-like molecules via a serine protease-like active site.
| |||||||||||
References
A) 1WAB. Protein Database, 1997. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/1WAB B) Ho, Y. S.; Sewnson, L.; Derewenda, U.; Serre, L.; Wei, Y.; Dauter, Z.; Hattori, M.; Adachi, T.; Aoki, J.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K.; Derewenda, Z. S. Brain acetylhydrolase that inactivates platelet-activating factor is a G-protein-like trimer. Nature, 1997, 385, 89-93. https://www.nature.com/articles/385089a0 https://www.nature.com/articles/385089a0 C) Miesfeld, R. L.; McEvoy, M. M. Biochemistry, 2nd ed.; W. W. Norton & Company, 2021. D) SGNH hydrolase superfamily. InterPro, 2017. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/InterPro/IPR036514/ E) Molgaard, A.; Kauppinen, S.; Larsen, S. Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases. Struct., 2000, 8(4), 373-383. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969212600001180?via%3Dihub F) 4Q7Q. Protein Database, 2014. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4Q7Q G) Rio, T. G. D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034). Stand. Genomic. Sci., 2010, 2(1), 87-95. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3035255/ H) Akoh, C. C.; Lee, G.; Liaw, Y.; Huang, T.; Shaw, J. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog. Lipid Res., 2004, 43(6), 534-552. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15522763/ I) 7BXD. Protein Database, 2021. https://www.rcsb.org/structure/7BXD J) Madej,T.; Lanczycki, C. J.; Zhang, D.; Thiessen, P. A.; Geer, R. C.; Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bryant, S. H. MMDB and VAST+: tracking structural similarities between macromolecular complexes. Nucleic Acids Res., 2014, 42(Database), D297-303. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1208