We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox: 5VKQ
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
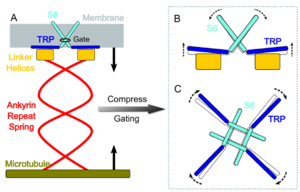
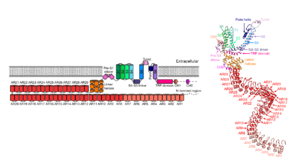
| - | The NOMPC (No | + | The NOMPC (<u>No</u> <u>m</u>echanoreceptor <u>p</u>otential <u>C</u>) is a mechanosensitive ion channel essential for hearing, touch and locomotion ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proprioception proprioception]) in ''Drosophila melanogaster''. It responds directly to mechanical stimuli such as pressure and stretch, converting physical forces into electrical signals. NOMPC is classified as a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transient_receptor_potential_channel transient receptor potential] (TRP) channel, a superfamily of membrane bound proteins involved with stimulus detection and sensory [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_transduction transduction] in various animal cells. When first discovered, NOMPC introduced a novel class of receptors, the TRP'''N'''. Although it was first described in ''Drosophila melanogaster'' <ref>PMID:10744543</ref>, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_homology homologs] of NOMPC were found in other animals, including the nematode worm ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' and the zebrafish. |
<scene name='10/1083740/Homotetramer_0/1'>(Click to reset the protein view.)</scene> | <scene name='10/1083740/Homotetramer_0/1'>(Click to reset the protein view.)</scene> | ||
Revision as of 20:54, 22 June 2025
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Walker RG, Willingham AT, Zuker CS. A Drosophila mechanosensory transduction channel. Science. 2000 Mar 24;287(5461):2229-34. PMID:10744543 doi:10.1126/science.287.5461.2229
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Jin P, Bulkley D, Guo Y, Zhang W, Guo Z, Huynh W, Wu S, Meltzer S, Cheng T, Jan LY, Jan YN, Cheng Y. Electron cryo-microscopy structure of the mechanotransduction channel NOMPC. Nature. 2017 Jul 6;547(7661):118-122. doi: 10.1038/nature22981. Epub 2017 Jun 26. PMID:28658211 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature22981
- ↑ Mascarenhas NM, Gosavi S. Understanding protein domain-swapping using structure-based models of protein folding. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2017 Sep;128:113-120. PMID:27867057 doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2016.09.013
- ↑ InterPro (IPR002110). Ankyrin repeat. Available at: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/InterPro/IPR002110/. Accessed on 2025 June 19.
- ↑ Li J, Mahajan A, Tsai MD. Ankyrin repeat: a unique motif mediating protein-protein interactions. Biochemistry. 2006 Dec 26;45(51):15168-78. PMID:17176038 doi:10.1021/bi062188q
- ↑ Wang Y, Guo Y, Li G, Liu C, Wang L, Zhang A, Yan Z, Song C. The push-to-open mechanism of the tethered mechanosensitive ion channel NompC. Elife. 2021 Jun 8;10:e58388. PMID:34101577 doi:10.7554/eLife.58388
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Hehlert P, Effertz T, Gu RX, Nadrowski B, Geurten BRH, Beutner D, de Groot BL, Göpfert MC. NOMPC ion channel hinge forms a gating spring that initiates mechanosensation. Nat Neurosci. 2025 Feb;28(2):259-267. PMID:39762662 doi:10.1038/s41593-024-01849-3
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Cheng LE, Song W, Looger LL, Jan LY, Jan YN. The role of the TRP channel NompC in Drosophila larval and adult locomotion. Neuron. 2010 Aug 12;67(3):373-80. PMID:20696376 doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2010.07.004
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Yan Z, Zhang W, He Y, Gorczyca D, Xiang Y, Cheng LE, Meltzer S, Jan LY, Jan YN. Drosophila NOMPC is a mechanotransduction channel subunit for gentle-touch sensation. Nature. 2013 Jan 10;493(7431):221-5. PMID:23222543 doi:10.1038/nature11685
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Effertz T, Wiek R, Göpfert MC. NompC TRP channel is essential for Drosophila sound receptor function. Curr Biol. 2011 Apr 12;21(7):592-7. PMID:21458266 doi:10.1016/j.cub.2011.02.048
- ↑ Schüler A, Schmitz G, Reft A, Özbek S, Thurm U, Bornberg-Bauer E. The Rise and Fall of TRP-N, an Ancient Family of Mechanogated Ion Channels, in Metazoa. Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Jun 22;7(6):1713-27. PMID:26100409 doi:10.1093/gbe/evv091