Prion protein
From Proteopedia
Kurt Giles (Talk | contribs)
(New page: The prion protein (PrP) is a cell surface glycoprotein. The cellular isoform (PrPC) is predominantly α-helical, but can undergo a structural conversion to a β-sheet rich conformation, te...)
Next diff →
Revision as of 10:44, 9 December 2008
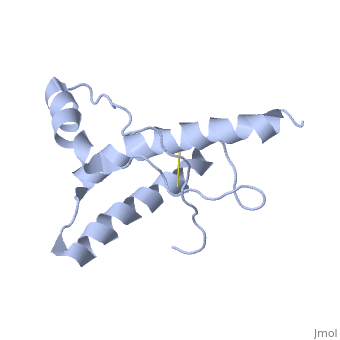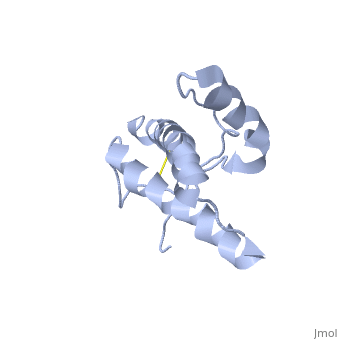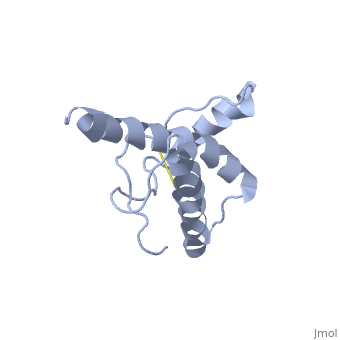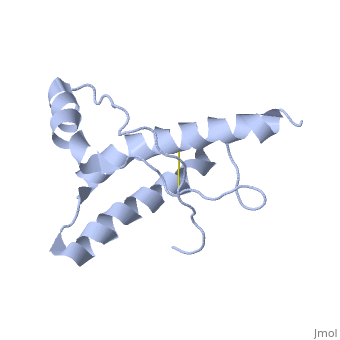
The prion protein (PrP) is a cell surface glycoprotein. The cellular isoform (PrPC) is predominantly α-helical, but can undergo a structural conversion to a β-sheet rich conformation, termed PrPSc. Prion diseases such as Creutzfeldt Jakob disease (CJD) in people, and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) commonly known as "mad cow" disease, are characterterized by aggregates of PrPSc
's normal cellular function is debated, and "knockout" mice lacking PrP are phenotypically normal.
has a predominantly α-helical structure and is localized to the outer leaflet of the cell membrane by a glycolipid anchor. In prion diseases PrPC undergoes a major structural transformation converting . This process is autocatalytic with PrPSc driving the refolding of PrPC in a template-dependent manner, leading to accumulation of PrPSc and ultimately neuronal cell death.
Structure of PrPC
| |||||||||
| 1hjm, 1 NMR models () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Related: | 1e1g, 1e1j, 1e1p, 1e1s, 1e1u, 1e1w, 1hjn | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Kurt Giles, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky, Michal Harel, Claudio Garutti, Eran Hodis