User:Eduardo Soares/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
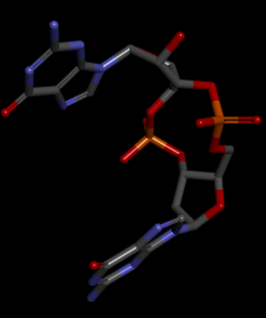
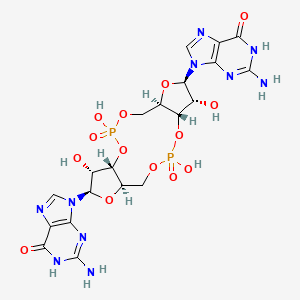
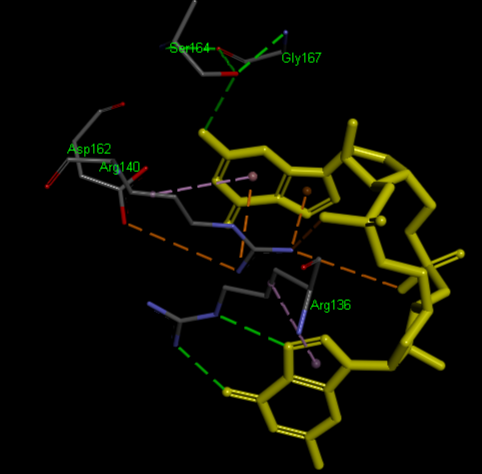
VCA0042/plzD complexed with c-di-GMP
Introduction
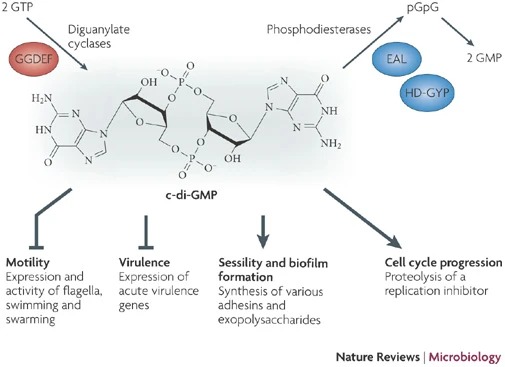
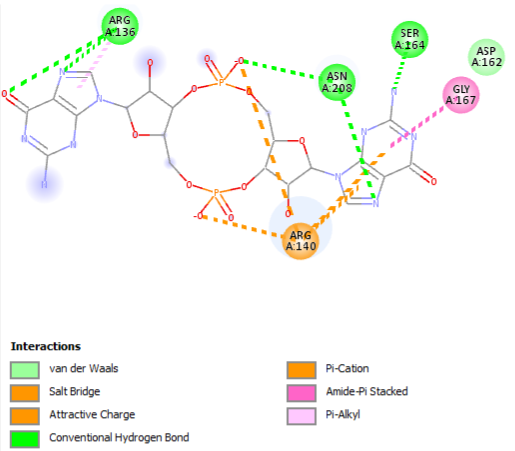
The PDB code 2RDE represents a PilZ protein complexed with cyclic diguanylate monophosphate (c-di-GMP) in Vibrio cholera there is a molecular interaction involved in the regulation of bacterial biofilm formation and motility. The complex is formed by the binding of the small signaling molecule c-di-GMP to a protein domain known as PilZ. This interaction plays a crucial role in bacterial physiology and is implicated in various cellular processes. [1]
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Benach J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.
- ↑ Pecina, Anna, et al. The Stand-Alone PilZ-Domain Protein MotL Specifically Regulates the Activity of the Secondary Lateral Flagellar System in Shewanella putrefaciens. Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 12, 2021. Frontiers, https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.668892.
- ↑ Bena
 ch J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.
ch J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105. - ↑ Benach J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.
- ↑ Hengge, R. Principles of c-di-GMP signalling in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 7, 263–273 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2109<\ref>
Molecular Interaction
The PilZ domain is typically found in proteins associated with type IV pili and other c-di-GMP-regulated processes. When c-di-GMP is present in the bacterial cell, it can bind to the PilZ domain, leading to conformational changes in the protein structure. This conformational change can result in alterations in protein-protein interactions or changes in protein activity, ultimately affecting the downstream processes regulated by the PilZ-containing protein. <ref> Purificação, Aline Dias da, et al. The World of Cyclic Dinucleotides in Bacterial Behavior. Molecules, vol. 25, n. 10, Janeiro de 2020, p. 2462. www.mdpi.com, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102462. </li> <li id="cite_note-5">[[#cite_ref-5|↑]] Purificação, Aline Dias da, et al. The World of Cyclic Dinucleotides in Bacterial Behavior. Molecules, vol. 25, n. 10, Janeiro de 2020, p. 2462. www.mdpi.com, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102462. </li>
<li id="cite_note-6">[[#cite_ref-6|↑]] Benach J, Swaminathan SS, Tamayo R, Handelman SK, Folta-Stogniew E, Ramos JE, Forouhar F, Neely H, Seetharaman J, Camilli A, Hunt JF. The structural basis of cyclic diguanylate signal transduction by PilZ domains. EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5153-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601918. Epub 2007 Nov 22. PMID: 18034161; PMCID: PMC2140105.</li></ol></ref>