From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
Background
Human Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a immune protein often categorized under hematopoietins. Since its discoverey, it has been known by many names including: interferon-ß2 (IFN-ß2), 26-kD protein, B-cell stimulatory factor-2 (BSF-2), hepatocyte stimulating factor (HSF), cytotoxic T-cell differentiation factor (CDF), interleukin-HP1 (IL-HP1), monocyte-granulocyte inducer type 2 (MGI-2), and hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor (HPGF/HGF). It wasn't until December of 1988 that is was givin the final moniker of IL-6 (PDB: 1IL6).
Structure
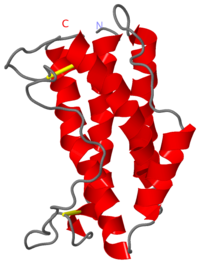
IL-6 is a monomer of 185 amino acids produced from T-Cells, macrophages, and endothelial cells found on a single gene at locus 7p21.
It contains five alpha-helices and four of these helices constitute a classical four-helix bundle with the fifth helix located in the CD loop.
Functions
IL-6 Receptor
Clinical Applications
Additional Resources
References