- Serine/threonine protein kinase 1 (Chk1) phosphorylates cdc25A, cdc25B and cdc25C. Upon phosphorylation, cdc25 binds adaptor protein and the cell is prevented from entering mitosis.
- Chk2 (Checkpoint kinase 2) phosphorylates cdc25C at Ser-216.
- Chk6 called also Aurora A is critical for the formation of mitotic spindles during cellular mitosis. Chk6 is phosphorylated at residues Thr287 and Thr288.
- Chk13 (Polo-like kinase 1 or Plk1) functions during the M phase of the cell cycle including the regulation of centrosome maturation and spindle assembly. Chk13 binds and phosphorylates proteins which are already phosphorylated on a motif recognized by its POLO-box domain (Pbd) at the C terminal. Human Chk13 contains catalytic domain (residues 13-345) and POLO-box domain (residues 345-603).
- Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase. GSK-3 is active in a number of intracellular signaling pathways. GSK-3 regulates glycogen synthase as well as other proteins. GSK-3 inhibition is studied as a therapeutic target in diseases like Alzheimer, diabetes, bipolar disorder and some cancers.
- B-Raf is related to retroviral oncogenes and participates in cellular signal transduction. B-Raf domains include the kinase domain - residues 444-721 and Ras-binding domain - residues 153-237. Mutated B-Raf was found in some human cancers. See more in B-RAF with PLX4032.
- c-Raf is part of the MAPK pathway. c-Raf domains include the kinase domain - residues 323-618, cysteine-rich domain – residues 136-187 and Ras-binding domain - residues 51-132. Mutations of c-Raf are possible causes of Noonan syndrome. For details on c-Raf see Molecular Playground/C-Raf.
For details on Snf1-related kinase see
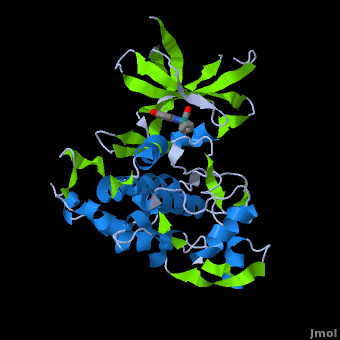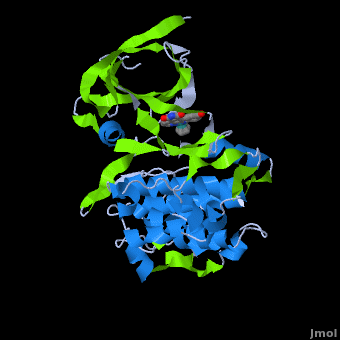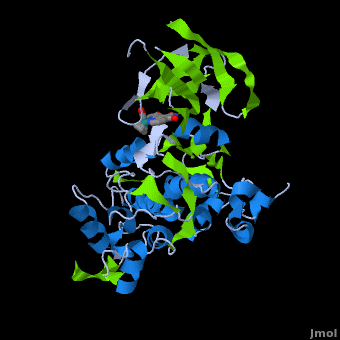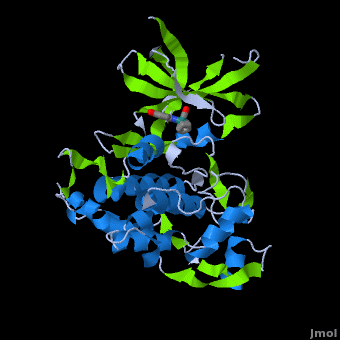
Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß [1]
A crystal structure of an bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several and . Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role. The unique, bulky molecular structure of the half-sandwich complex with the CO-ligand oriented perpendicular to the pyridocarbazole heterocycle allows the complex to stretch the whole distance and to interact tightly with . Although this complex is a conventional ATP-competitive binder, the unique shape of the complex allows novel interactions with the glycine-rich loop which are crucial for binding potency and selectivity. It can be hypothesized that coordination spheres which present other ligands towards the glycine-rich loop might display completely different protein kinase selectivities.