From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
Background
Human Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a immune protein often categorized under hematopoietins. Since its discoverey, it has been known by many names including: interferon-ß2 (IFN-ß2), 26-kD protein, B-cell stimulatory factor-2 (BSF-2), hepatocyte stimulating factor (HSF), cytotoxic T-cell differentiation factor (CDF), interleukin-HP1 (IL-HP1), monocyte-granulocyte inducer type 2 (MGI-2), and hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor (HPGF/HGF). It wasn't until December of 1988 that is was givin the final moniker of IL-6 (PDB: 1IL6). The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the receptor complex for IL6.
Structure
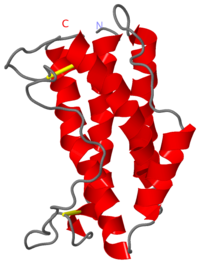
IL-6 is a monomer of 185 amino acids produced from T-Cells, macrophages, and endothelial cells found on a single gene at locus 7p21.
It contains five alpha-helices and four of these helices constitute a classical four-helix bundle with the fifth helix located in the CD loop. The four helices that form the four-helix bundle are arranged so that the helices A and B run in the same direction and C and D in the opposite direction. Linking the helices in this arrangement is made possible by a long loop joining the A and B helices, a short one between the B and C and finally a second long connection between C and the fourth main helix D.
Functions
Interleukin 6 (IL6) is a potent polyfunctional cytokine that plays a vital role in host defense. This is demonstrated by its potent ability to induce acute-phase responses in the liver.
IL-6 Receptor
Clinical Applications
Dysregulated production of IL6 and this receptor are implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as multiple myeloma, autoimmune diseases and prostate cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.
A good correlation has been found between levels of IL-6 and bone loss in patients with Paget's disease and multiple myeloma. In those patients, higher levels of IL-6 correlated to higher rates of bone loss. Additionally, IL-6 levels decreased with increasing levels of estrogen. These findings strongly suggest that IL-6 plays a key roll in post-menopausal bone loss.
Additional Resources
References