From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
| This Sandbox is Reserved from January 10, 2010, through April 10, 2011 for use in BCMB 307-Proteins course taught by Andrea Gorrell at the University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, BC, Canada.
|
To get started:
- Click the edit this page tab at the top. Save the page after each step, then edit it again.
- Click the 3D button (when editing, above the wikitext box) to insert Jmol.
- show the Scene authoring tools, create a molecular scene, and save it. Copy the green link into the page.
- Add a description of your scene. Use the buttons above the wikitext box for bold, italics, links, headlines, etc.
More help: Help:Editing
|
Introduction
(pronounced /ˈriːnɨn/ REE-nin) is also known as angiotensinogenase, a monospecific enzyme that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Renin is responsible for catalyzing the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of angiotensin II. Once renin and pro-renin bind to the pro-renin receptor, there is an increased enzymatic activity and additional physiological effects. [1]
Structure
Renin belongs in a family called aspartic proteases which use an aspartate residue for the catalysis of their peptide substrate. X-ray diffraction experiments has shown there is a striking similarity among the structures of aspartyl proteases. [2] Renin consists of two homologous lobes each containing an aspartic acid. Between the lobes is the active site, which is catalyzed by the aspartic acid residues, a characteristic trait of all aspartate proteases. [1] Renin in its full mature form has a mass of 37 kDa and contains 340 amino acids.[3]
Biochemistry
Renin is an aspartyl protease. [4]
Function
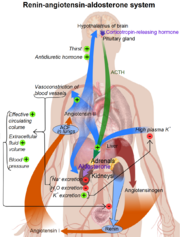
Renin plays a key role in the Renin-Angiotension sysmtem (RAS). This system is responsible for the control of blood pressure and salt balances in mammals.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gradman AH, Kad R. Renin inhibition in hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Feb 5;51(5):519-28. PMID:18237679 doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.10.027
- ↑ K Akahane, H Umeyama, S Nakagawa, I Moriguchi, S Hirose, K Iizuka, and K Murakami. "Three-dimensional structure of human renin". Hypertension. 1985;7:3-12
- ↑ Armstrong C. The vision of the pore. Science. 1998 Apr 3;280(5360):56-7. PMID:9556453
- ↑ Inagami T. Structure and function of renin. J Hypertens Suppl. 1989 Apr;7(2):S3-8. PMID:2666611