Background
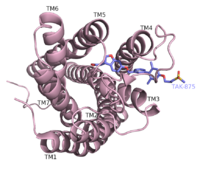
Human G-protein coupled receptor 40 (hGPR40) is a seven helical transmembrane domain receptor for long-chain free fatty acids that slimutates insulin secretion (Srivastava). This enzyme is primarily located in the pancreatic b-cells in the islets of Langerhans, and as such, it has become a target for potential Type II diabetes treatments (Kebede). Activation of hGPR40 has been shown to both stimulate insulin secretion and decrease glucose concentration (Ma, 2016). GPR40 is a member of a group of homologous GPCRs all located on chromosome 19q13.1 including GPR41, 42, and 43.
Structure
Binding Sites
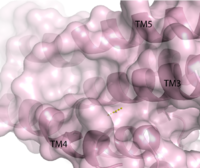
Figure 2. Second proposed binding site of GPR40. By visual inspection, a second possible binding site was proposed between transmembrane helices 3, 4, and 5 on the intracellular side.
Image:4phuBind3.png Figure 3. Third proposed binding site of GPR40. By visual inspection, a third possible binding site was proposed between transmembrane helices 1, 2, and 7 on the extracellular side.
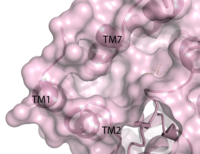
Figure 3. Third proposed binding site of GPR40. By visual inspection, a third possible binding site was proposed between transmembrane helices 1, 2, and 7 on the extracellular side.
Ionic Charge Network
ECL2
Function
Clinical Relevance
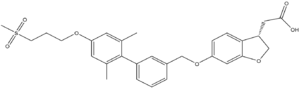
Tak-875