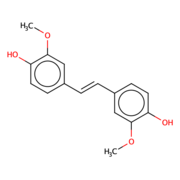
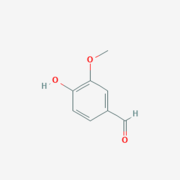
Lignostilbene-α,β-dioxygenase A (LsdA) is a catalytic enzyme found in bacteria to break down cellulose components.
Function
Lignostilbene-α,β-dioxygenase A (LsdA) is an enzyme found in the bacteria Sphingomonas paucimbilis.[1] It is used to catalyze the substrate, lignostilbene, into two vanillin molecules. Vanillin is a member of the benzaldehydes class and plays a role in the plant metabolite[2]. Lignin is found in the plant cell walls, lignocellulose, and it gives the plant its rigid structure. The depolymerization of the lignin can allow for better use of the plants resources as a source of biofuel.
Lignostilbene
Vanillin
Broader Implications
Energy Transformation
Structural highlights
with a clear view of the ligand Mg+2 and