Cavity programs
From Proteopedia
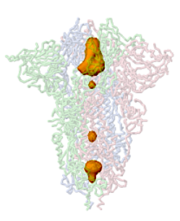
This page lists programs that identify and offer visualization options for cavities in macromolecules. Broadly, the term "cavities" includes pockets, tunnels and channels. A pocket is a depression in the surface with one entrance. A tunnel connects two or more locations, and may or may not have entrances from the surface[1][2]. Some cavities are buried with no entrances from the surface (example: 3drf).
Nearly all proteins have irregular surfaces with shallow pockets, mostly with no known functions. Some proteins have deep pockets, for example the catalytic anionic gorge in acetylcholinesterase (e. g. 1vot). Such a pocket can also be termed a tunnel accessing the catalytic site[1][2].
Programs are listed alphabetically.
Jmol
|
Jmol: |
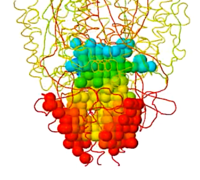
Jmol can identify and display pockets and cavities as isosurfaces. Examples are shown at Jmol/Cavities pockets and tunnels, where you will also find explanations of the interior cavity and pocket commands.
Jmol has an extensive command language that provides great flexibility in visualizing cavities.
The Jmol Java standalone application is downloadable from jmol.org. It is also available as JSmol, a Javascript implementation used in most pages in Proteopedia.
Jmol is updated many times each year.
PACUPP
|
PACUPP:
|
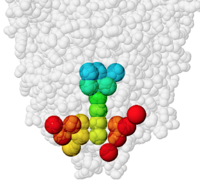
PACUPP, Pockets And Cavities Using Pseudoatoms in Proteins, identifies cavities by filling them with pseudoatoms (holmium, Ho, think "holes"). An example is presented in some detail at PACUPP: Pockets And Cavities Using Pseudoatoms in Proteins. Further examples with demonstrations of how to use PACUPP are in a YouTube video and a slideshow, available from molviz.org/pacupp, where you can also download the program.
PACUPP offers a number of simple commands specialized for visualizing cavities, mostly single letter commands. Some call up a dialog where the use enters information. Lists cavity-lining atoms in a spreadsheet-ready text file. Learning the PACUPP commands is much easier than learning Jmol commands.
PACUPP is a Jmol script. It processes 2/3 of the entries in the Protein Data Bank in ≤15 sec each. For large models such as ribosomes or proteasomes that may take many minutes, PACUPP offers an unattended batch mode.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Marques SM, Daniel L, Buryska T, Prokop Z, Brezovsky J, Damborsky J. Enzyme Tunnels and Gates As Relevant Targets in Drug Design. Med Res Rev. 2017 Sep;37(5):1095-1139. doi: 10.1002/med.21430. Epub 2016 Dec 13. PMID:27957758 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/med.21430
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kingsley LJ, Lill MA. Substrate tunnels in enzymes: structure-function relationships and computational methodology. Proteins. 2015 Apr;83(4):599-611. doi: 10.1002/prot.24772. Epub 2015 Feb 28. PMID:25663659 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/prot.24772