Function
The Cat Eye Syndrome Chromosome Region Candidate 2 (CECR2) is the regulatory subunit of the ATP-dependent CERF-1 and CERF-5 ISWI chromatin remodeling complexes that modulate nucleosome spacing and DNA accessibility during replication and transcription.[1][2][3][4]. CECR2 also plays a key role in the DNA damage repair response, as it inhibits γ-H2AX activity.[5]. CECR2 is involved in various processes during development, including embryogenesis and spermatogenesis.[6][7]. Recent studies have identified CECR2 as an epigenetic regulator of NF-kB pro-inflammatory gene expression through the recognition of acetylated RelA and driving breast cancer metastasis.[8]
Domain Organization
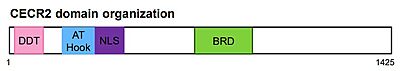
CECR2 is composed of a DDT domain, an AT hook, an NLS, and a bromodomain.
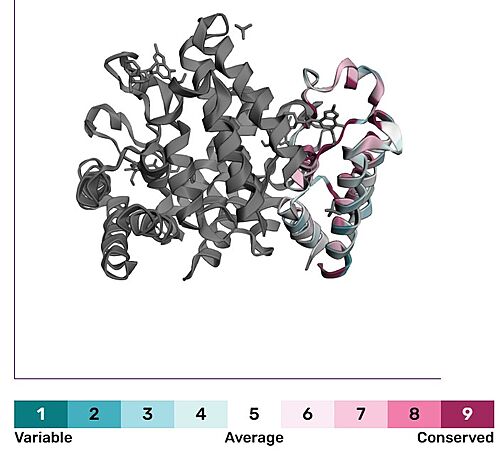
Sequential and Structural Conservation
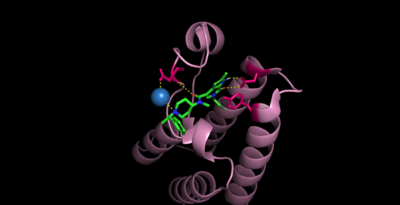
Bromodomains
Bromodomains are composed of 4 alpha helices (, and 2 loops (ZA and BC). There are typically 4 conserved water molecules found within the acetyllysine binding pocket of the bromodomain. The two loops contain the majority of the residues responsible for ligand coordination, including the located in the BC loop. In addition, there is a hydrophobic shelf found before the before the ZA loop and following αZ helix. There is also a that corresponds to the first residue found in the αC that is usually hydrophobic. Histone acetyllysines form a hydrogen bond with the conserved asparagine of bromodomains while various other residues make polar contacts to stabilize the interaction, directly or indirectly.
Disease and Therapeutics
These contacts in CECR2. N514, D464, Y520 (no contact) [9]