Citric Acid Cycle
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*[[Krebs cycle overview]] | *[[Krebs cycle overview]] | ||
*[[Krebs cycle reactions]] | *[[Krebs cycle reactions]] | ||
| + | *[[Major metabolic pathways converging on the citric acid cycle]] | ||
| + | *[[Citric acid cycle intermediates serve as substrates for biosynthetic processes]] | ||
| + | |||
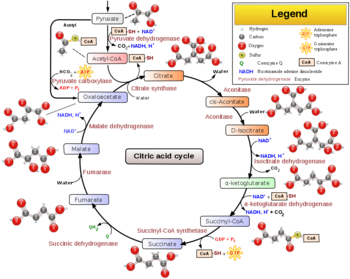
The [[Citric Acid Cycle]] (tricarboxylic acid cycle) is a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions which are critical in cellular respiration. Under oxidative conditions, pyruvate continues to be metabolized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In this cycle, Acetyl-CoA, a byproduct of [[glycolysis]], along with various cofactors, are broken down into carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of GTP and NADH. | The [[Citric Acid Cycle]] (tricarboxylic acid cycle) is a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions which are critical in cellular respiration. Under oxidative conditions, pyruvate continues to be metabolized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In this cycle, Acetyl-CoA, a byproduct of [[glycolysis]], along with various cofactors, are broken down into carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of GTP and NADH. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 58: | ||
*Step 6 = [[Krebs cycle step 5]] | *Step 6 = [[Krebs cycle step 5]] | ||
Succinyl-CoA => <scene name='43/430893/Cv/10'>Succinate</scene> | Succinyl-CoA => <scene name='43/430893/Cv/10'>Succinate</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The succinyl-CoA formed during [[Beta oxidation]] can also enter the Citric Acid Cycle in this step. | ||
'''Step 7 - Oxidation - Succinate dehydrogenase''' | '''Step 7 - Oxidation - Succinate dehydrogenase''' | ||
| Line 70: | Line 75: | ||
*Step 9 = [[Krebs cycle step 8]] | *Step 9 = [[Krebs cycle step 8]] | ||
L-Malate => <scene name='43/430893/Cv/3'>oxaloacetate</scene> | L-Malate => <scene name='43/430893/Cv/3'>oxaloacetate</scene> | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | Oxaloacetate takes part in [[gluconeogenesis]], the urea cycle, the glyoxylate cycle, amino acid synthesis ([[Oxaloacetate/aspartate: lysine, asparagine, methionine, threonine, and isoleucine]]), [[fatty acid synthesis]]. | ||
'''Step 10 / 0 - Aldol condensation - Citrate synthase''' | '''Step 10 / 0 - Aldol condensation - Citrate synthase''' | ||
| Line 76: | Line 82: | ||
*Step 10 / 0 = [[Krebs cycle step 1]] | *Step 10 / 0 = [[Krebs cycle step 1]] | ||
4C <scene name='43/430893/Cv/3'>oxaloacetate</scene> to a 6C molecule <scene name='43/430893/Cv/4'>citrate</scene> | 4C <scene name='43/430893/Cv/3'>oxaloacetate</scene> to a 6C molecule <scene name='43/430893/Cv/4'>citrate</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Major metabolic pathways converging on the citric acid cycle]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Citric acid cycle intermediates serve as substrates for biosynthetic processes]] | ||
To view automatically seeded indices concerning [[Citric Acid Cycle]] See: | To view automatically seeded indices concerning [[Citric Acid Cycle]] See: | ||
Current revision
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Ann Taylor, Wayne Decatur, Jaime Prilusky