Introduction
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by extracellular proteic plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles.[1] These plaques are collections of fibrils consisting mostly of beta-amyloid of aggregated beta-sheets. The oxidative stress that an affected brain is under is further proof of the toxicity of amyloid beta. When amyloid beta is in contact with metal ions and oxygen reactive oxygen species (especially hydrogen peroxide) are created.[2] Amyloid beta also maintains the capacity to to induce pore formation in neuronal and endothelial cells which can trigger cell death.[1][2] The final source of amyloid beta toxicity stems from its ability to induce endothelial cell damage through the production of superoxide, though the mechanism of such induction is unclear.[2]
Structure
Amyoloid beta is actually the of the which is a type I membrane-spanning glycoprotein encoded on chromosome 21 [APP].[2] Amyloid beta results from an abnormal cleavage by beta-secretase at the N-terminal and gamma-secretase at the C-terminal[[1]]. The cleavage is nonspecific and results in peptides 39-43 amino acids in length, with 42 being the most common. Such cleavages occur most commonly in the plasma membrane is also occurs in neuronal membranes.[2]
The first 16 residues, Asp-Ala-Glu-Phe-Arg-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Glu--Val-His-His-Gln-Lys, are mostly hydrophobic while form a binding domain for Cu(II). Residues 12-23 function as the region allowing for the formation of dimers and/or oligomers. This region also serves as the binding site for cholesterol, apolipoproteinE, alpha7nAChr, and amyloid beta-peptide binding alcohol dehydrogenase.[2]
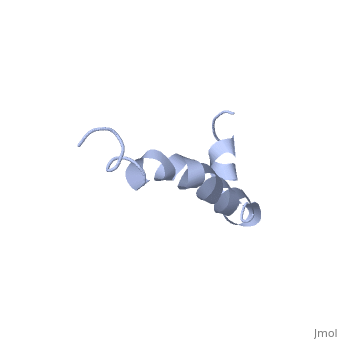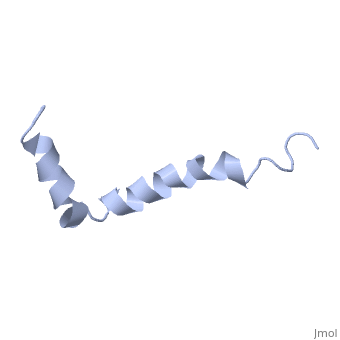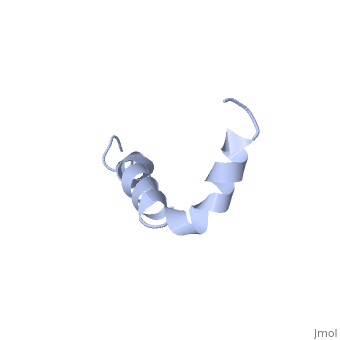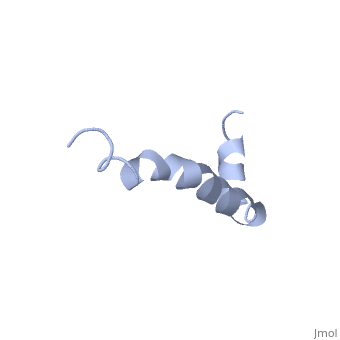
The most reasonable structure determined structure consists of ; the first helix (residues 8-25) is well defined and has an RMSD of 0.38 angstroms and the second (residues 28-38) is interrupted at the Ile32-Gly33 connection. The second helix corresponds to the transmembrane region of APP and thus contains multiple small and hydrophobic amino acids. The two helices are connected by a (residues 26 and 27).[1]
The toxicity of amyloid beta is due to the formation of aggregates and oligomers. The actual structures of these oligomers is unknown but is likely similar to that of amyloid beta in mature plaques.[1]
Neurotoxicity
Generation of Radicals
Amyloid beta produces reactive oxygen species, which induces oxidative stress and inflammation.[2]
Pore Formation
Amyloid beta can adhere to endothelial cell walls and create lesions, eventually a large deposite will cause cerrbral hemorrhage. The pores cause loss of calcium homeostasis and an influx of Ca2+ into neurons.[2]
Interaction with tau
Tau proteins function to stabilize microtubules [[2]]. Association between Tau proteins and amyloid beta results in dissociation of tau from microtubules which collapses the axonal structure leading to the death of neurons.[2]
Binding ApoE
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Crescenzi O, Tomaselli S, Guerrini R, Salvadori S, D'Ursi AM, Temussi PA, Picone D. Solution structure of the Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide (1-42) in an apolar microenvironment. Similarity with a virus fusion domain. Eur J Biochem. 2002 Nov;269(22):5642-8. PMID:12423364
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 Rauk A. Why is the amyloid beta peptide of Alzheimer's disease neurotoxic? Dalton Trans. 2008 Mar 14;(10):1273-82. Epub 2008 Feb 12. PMID:18305836 doi:10.1039/b718601k