Acid-beta-glucosidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaucher's_disease Gaucher disease]is the most common lysosomal storage disease, and is associated with mutations in the gene coding for the enzyme acid-β-glucosidase ([http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/ enzyme classification] E.C. 3.2.1.45). | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaucher's_disease Gaucher disease]is the most common lysosomal storage disease, and is associated with mutations in the gene coding for the enzyme acid-β-glucosidase ([http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/ enzyme classification] E.C. 3.2.1.45). | ||
| - | There are ~200 known mutations, mostly missense mutations which result in substitution of amino acids in the protein. Some mutations cause complete deactivation of the enzyme; others impair its stability, and some affect both activity and stability. There are three known phenotypes of the disease: a mild, severe and acute. The acute phenotype is neuropathic, while severe and mild symptoms are caused by accumulation of GlcCer in macrophage cells resulting in bone atrophy, spleen enlargement, etc. | + | There are ~200 known mutations, mostly missense mutations which result in substitution of amino acids in the protein. Some mutations cause complete deactivation of the enzyme; others impair its stability, and some affect both activity and stability. There are three known phenotypes of the disease: a mild, severe and acute. The acute phenotype is neuropathic, while severe and mild symptoms are caused by accumulation of GlcCer in macrophage cells resulting in bone atrophy, spleen enlargement, etc.<ref>PMID:23233555</ref> |
There are two available treatments for the disease: an enzyme replacement therapy and a substrate reduction therapy. | There are two available treatments for the disease: an enzyme replacement therapy and a substrate reduction therapy. | ||
Revision as of 07:41, 23 December 2015
| |||||||||||
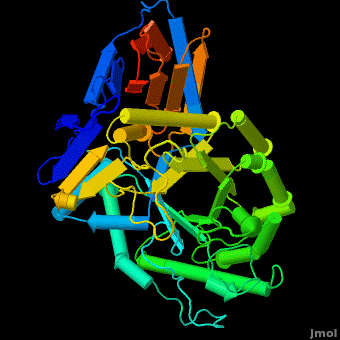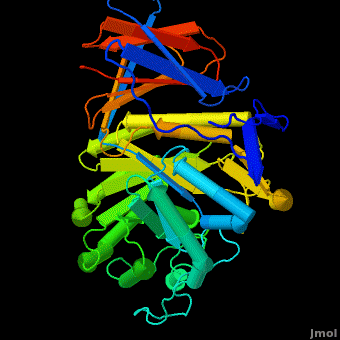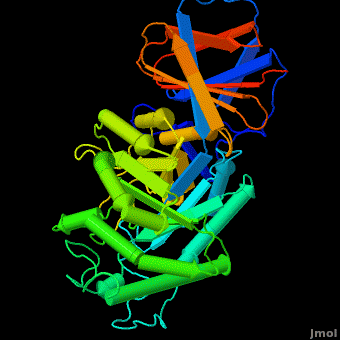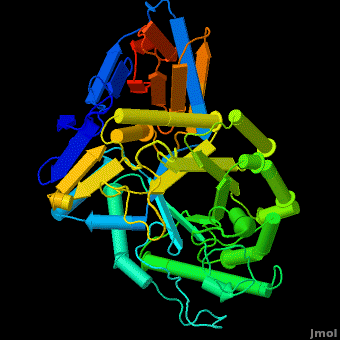
3D structures of Acid-β-glucosidase
Updated on 23-December-2015
2wkl, 3gxd, 3gxi, 3gxm, 2v3f, 2nt0, 2nt1, 2j25, 2f61, 1ogs, 3rik – hABG – human
3ke0, 3keh – hABG (mutant)
2wcg, 3gxf, 2vt0, 2v3e, 2v3d, 1y7v, 3ril – hABG + inhibitor
2nsx – hABG + pharmacological chaperone
2xwd, 2xwe – hABG + nojirimycin derivative
References
- ↑ Dvir H, Harel M, McCarthy AA, Toker L, Silman I, Futerman AH, Sussman JL. X-ray structure of human acid-beta-glucosidase, the defective enzyme in Gaucher disease. EMBO Rep. 2003 Jul;4(7):704-9. PMID:12792654 doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor873
- ↑ Grabowski GA. Gaucher disease and other storage disorders. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012;2012:13-8. doi:, 10.1182/asheducation-2012.1.13. PMID:23233555 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2012.1.13
Additional Resources
Metabolic Disorders
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Treatment of Gaucher disease
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Boris Brumshtein, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Eran Hodis, David Canner