Sandbox reserved 659
From Proteopedia
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:Picture4.png|thumb|right|260px|frame|Whey protein powder]] | [[Image:Picture4.png|thumb|right|260px|frame|Whey protein powder]] | ||
[[Image:Picture6.jpg|thumb|right|260px|frame|Whey production process]] | [[Image:Picture6.jpg|thumb|right|260px|frame|Whey production process]] | ||
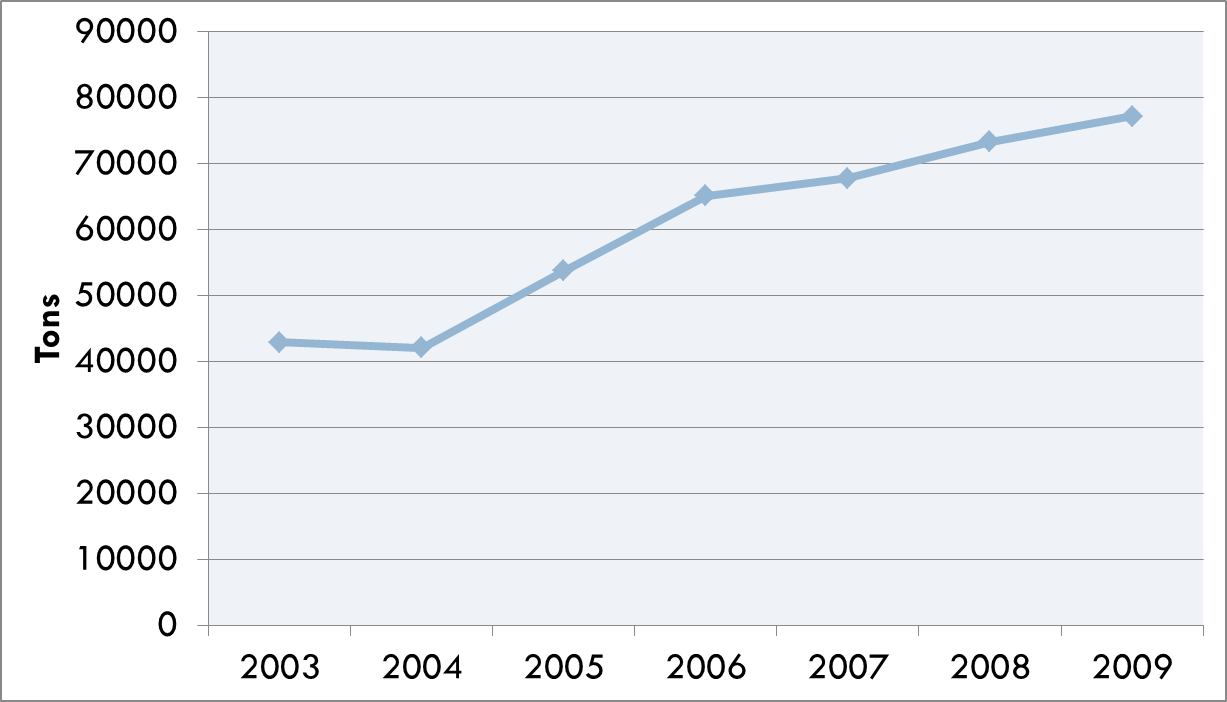
| - | [[Image:Picture3.png|thumb|center| | + | [[Image:Picture3.png|thumb|center|100px|frame|Whey protein production in tons. Gould, 2010]] |
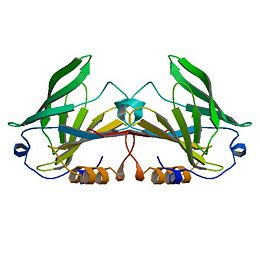
<StructureSection load='1B8E' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Beta Lactoglobulin (PDB entry [[1B8E]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1B8E' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Beta Lactoglobulin (PDB entry [[1B8E]])' scene=''> | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 27 November 2012
Beta Lactoglobulin
β-Lactoglobulin(β-LG) is the bulk constituent of whey protein in most ruminant species and is also present in the milks of most mammalian species, although not in rodent, human, and lagomorph milks. It has been studied extensively for some time ( Tilley, 1960; Lyster, 1972; Kinsella and Whitehead, 1987; Hambling et al., 1992; Sawyer, 2003). β-LG is a lipocalin as is seen through its amino-acid sequence and structure (Flower et al., 2000). Lipocalins are a varied family which bind small hydrophobic ligands, and often act as transporters in vivo. The purpose of β-LG, however, is not clear. Genetic variants of β-LG expressing genes have been reported, especially in cows and several nonruminant species (Kontopidis, 2004).
Whey is an often used food ingredient in the food industry and has many useful functional characteristics including foaming, gelling, thermal stability, emulsification, and protein fortification. It has also been suggested that it has many useful health benefits including exercise recovery, weight management, cardiovascular health, anti-cancer effects, anti-infection activity, wound repair, and infant nutrition. Human consumption of whey ingredients has steadily increased and has become more and more important to the dairy industry. An issue with whey ingredients is the subtle off flavor often associated with whey proteins. During the Cheddar cheese making process, norbixin leaches into the whey during the draining of the curd. Norbixin, a carotenoid extracted from the bixa orellana seed and added to cheese milk to give Cheddar its expected yellow flavor, would also contribute yellow color to the final product into which the whey ingredient is added. To prevent discoloration of the final product, whey is bleached by either hydrogen peroxide or benzoyl peroxide. In addition to a white color, this also causes lipid oxidation and associated off flavors.
| |||||||||||
Physiological Function of β-LG
| |||||||||||
Tanford Transition of β-LG
| |||||||||||