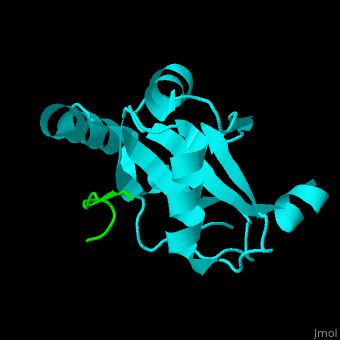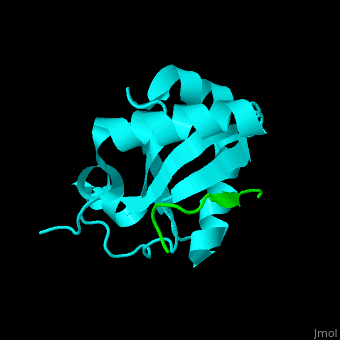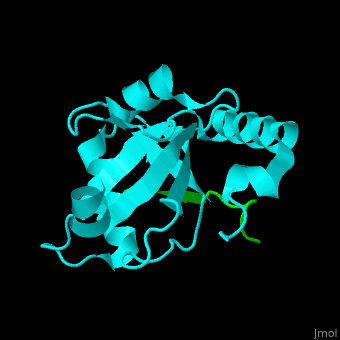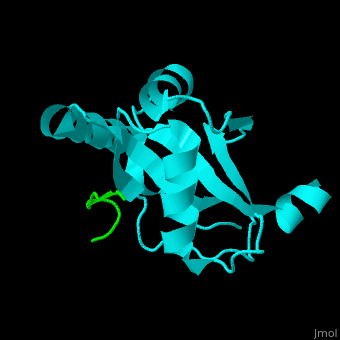Microtubule-associated protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human microtubule-associated protein light chain 3B (cyan) complex with sequestosome peptide (green) (PDB code [[2zjd]])' scene='70/708075/Cv/1'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3''' (LC3) is recruited to autophagosomal membranes during autophagy<ref>PMID:7480164</ref>. The human LC3B is cleaved after synthesis to expose a C-terminal glycine which binds via a phospholipid anchor to autophagosomal vesicle membranes during autophagy. Thus detection of LC3 is a reliable method for monitoring autophagy. The microtubule-associated proteins are classified as 2 types. Type 1 includes MAP1 and type 2 includes MAP2, MAP4 and [[Tau protein]]. | '''Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3''' (LC3) is recruited to autophagosomal membranes during autophagy<ref>PMID:7480164</ref>. The human LC3B is cleaved after synthesis to expose a C-terminal glycine which binds via a phospholipid anchor to autophagosomal vesicle membranes during autophagy. Thus detection of LC3 is a reliable method for monitoring autophagy. The microtubule-associated proteins are classified as 2 types. Type 1 includes MAP1 and type 2 includes MAP2, MAP4 and [[Tau protein]]. | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 23 July 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of microtubule-associated protein
Updated on 23-July-2017
References
- ↑ Maccioni RB, Cambiazo V. Role of microtubule-associated proteins in the control of microtubule assembly. Physiol Rev. 1995 Oct;75(4):835-64. PMID:7480164
- ↑ Halpain S, Dehmelt L. The MAP1 family of microtubule-associated proteins. Genome Biol. 2006;7(6):224. PMID:16938900
- ↑ Lebouvier T, Scales TM, Williamson R, Noble W, Duyckaerts C, Hanger DP, Reynolds CH, Anderton BH, Derkinderen P. The microtubule-associated protein tau is also phosphorylated on tyrosine. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;18(1):1-9. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2009-1116. PMID:19542604 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2009-1116
- ↑ Schraen-Maschke S, Dhaenens CM, Delacourte A, Sablonniere B. Microtubule-associated protein tau gene: a risk factor in human neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Dis. 2004 Apr;15(3):449-60. PMID:15056452 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2003.12.009
- ↑ Ichimura Y, Kumanomidou T, Sou YS, Mizushima T, Ezaki J, Ueno T, Kominami E, Yamane T, Tanaka K, Komatsu M. Structural basis for sorting mechanism of p62 in selective autophagy. J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 15;283(33):22847-57. Epub 2008 Jun 4. PMID:18524774 doi:http://dx.doi.org/M802182200
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky