Acid-beta-glucosidase
Acid-beta-glucosidase or glucosylceramidase is a lysozomal enzyme (EC number 3.2.1.45), which cleaves glucosylceramide to glucose and ceramide. It acts through an acid-base hydrolysis.
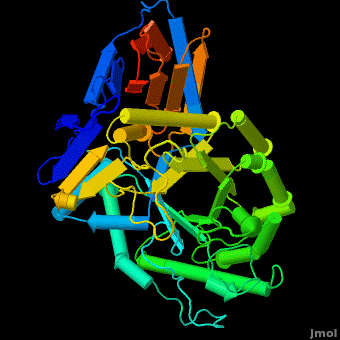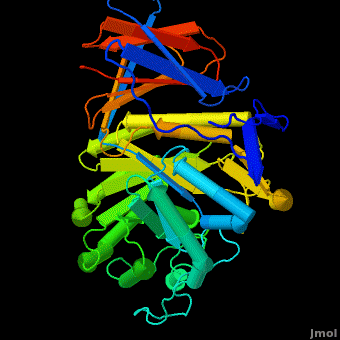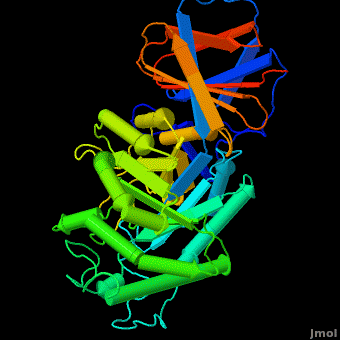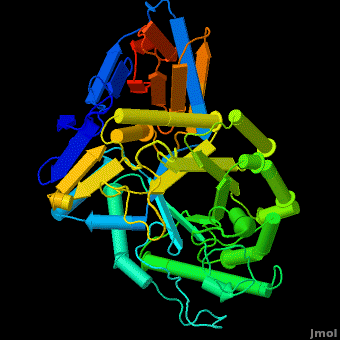
The enzyme is a lysosomal, membrane-associated glycoprotein, and its 3D structure revealed that its catalytic domain is a TIM barrel. It catalyzes hydrolysis of the sphingolipid, , to at the acidic pH prevailing within the lysosome. .
According to the mechanism, an enzyme, which acts through the acid-base reacion has to contain in the a proton donor, an acid, and a nuclophile - the base. The nuclophile is involved in formation and stabilization of the intermediate state, were a proton is transferred from an anomeric carbon to the leaving group. At that stage, the proton donor would donate its proton to the intermediate complex, releasing the second product and hence acting as a catalytic acid. Such a mechanism depends strongly on the pH of the environment. Fine changes in acidity of the solution might affect the ionization states of the residues involved in the catalysis. Therefore there would be a strong dependence of the enzyme's activity on the pH of the solution. Some additional details in
Several x-ray structures of the enzyme have been solved. PDB codes:
1ogs - the first structure of acid-beta-glucosidase, the enzyme involved in Gacher disease. Structure of deglycosylated Cerezyme™. [1]
2f61; 2nt0; 2nt1; 2v3d; 2v3e; 2v3f; 2nsx; 2j25
1y7v - acid-beta-glucosidase conjugated with an irreversible inhibitor, conduritol-B-epoxide (CBE);
The entrance to the active site of the enzyme is confined by three loops (Loop-1, residues 346-349; Loop-2, 393-399; Loop-3, 312-319), which have been observed in a number of conformations. Loop-1 is found to be involved in crystal contact interactions between the two individual protein molecules in crystals. Its conformation was not found to change significantly in various crystals of the enzyme. In contrast, loops-2 and 3 were detected in several different stable conformations, and displayed varying conformations in different structures even in the absence of an inhibitor in the active site. These loops were found to change the shape of the entrance as well as several properties of the active site.
Gaucher disease
Gaucher diseaseis the most common lysosomal storage disease, and is associated with mutations in the gene coding for the enzyme acid-β-glucosidase (enzyme classification E.C. 3.2.1.45).
There are ~200 known mutations, mostly missense mutations which result in substitution of amino acids in the protein. Some mutations cause complete deactivation of the enzyme; others impair its stability, and some affect both activity and stability. There are three known phenotypes of the disease: a mild, severe and acute. The acute phenotype is neuropathic, while severe and mild symptoms are caused by accumulation of GlcCer in macrophage cells resulting in bone atrophy, spleen enlargement, etc.[2]
There are two available treatments for the disease: an enzyme replacement therapy and a substrate reduction therapy.
In enzyme replacement therapy a recombinant enzyme (Cerezyme™) is produced by the Genzyme company and intra-venously injected to patients. In a substrate reduction therapy a small molecule inhibitor (Zavesca™) is used to inhibit the synthesis of the accumulated glucosylceramide.
Cerezyme™ vs Plant produced enzyme in a Gaucher disease
Acid-beta-glucosidase for treatment of a Gaucher disease is produced in CHO cells (™) (1ogs;1y7v;2f61; 2nt0; 2nt1; 2v3d; 2v3e; 2nsx; 2j25) or in a carrot stem cells suspension (plant produced enzyme by Protalix biopharmaceuticals, 2v3d; 2v3f; 2v3e). Recently solved structures of both enzymes indicate the enzymes are virtually in their 3D structures. Yet some small insignificant differences in sugars arise due to the use of different expression systems.
3D structures of Acid-β-glucosidase
Acid-β-glucosidase 3D structures