We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Citric Acid Cycle
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*[[Krebs cycle overview]] | *[[Krebs cycle overview]] | ||
*[[Krebs cycle reactions]] | *[[Krebs cycle reactions]] | ||
| - | *[[Major metabolic pathways converging on the citric acid cycle]] | ||
| - | *[[Citric acid cycle intermediates serve as substrates for biosynthetic processes]] | ||
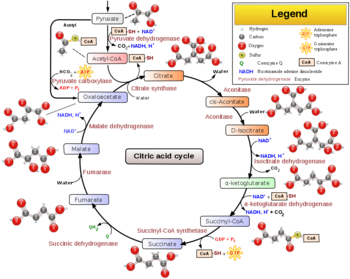
The [[Citric Acid Cycle]] (tricarboxylic acid cycle) is a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions which are critical in cellular respiration. Under oxidative conditions, pyruvate continues to be metabolized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In this cycle, Acetyl-CoA, a byproduct of [[glycolysis]], along with various cofactors, are broken down into carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of GTP and NADH. | The [[Citric Acid Cycle]] (tricarboxylic acid cycle) is a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions which are critical in cellular respiration. Under oxidative conditions, pyruvate continues to be metabolized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In this cycle, Acetyl-CoA, a byproduct of [[glycolysis]], along with various cofactors, are broken down into carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of GTP and NADH. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 49: | ||
*[[2-Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase]] | *[[2-Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase]] | ||
*Step 5 = [[Krebs cycle step 4]] | *Step 5 = [[Krebs cycle step 4]] | ||
| - | 5C α-Ketoglutarate => <scene name='43/430893/Cv/9'>Succinyl-CoA</scene> 4C chain (CoA excluded) | + | 5C α-Ketoglutarate => <scene name='43/430893/Cv/9'>Succinyl-CoA</scene> 4C chain (CoA excluded) |
'''Step 6 - Substrate-level phosphorylation - Succinyl-CoA synthetase''' | '''Step 6 - Substrate-level phosphorylation - Succinyl-CoA synthetase''' | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 16 February 2023
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Ann Taylor, Wayne Decatur, Jaime Prilusky