SUMO
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
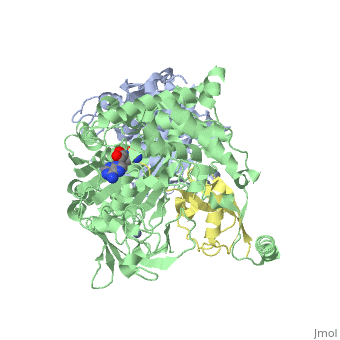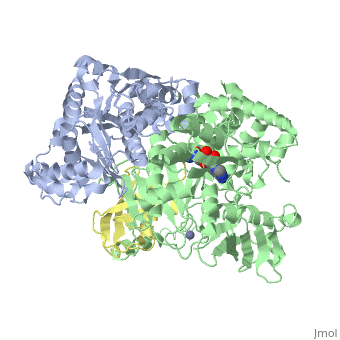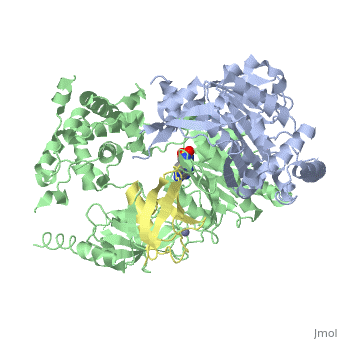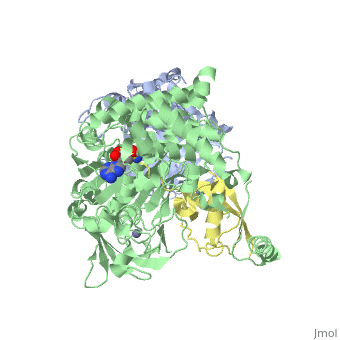
| - | [[SUMO]] is a '''Small Ubiquitin-like MOdifier''' which covalently attaches to cellular proteins to modify their function. SUMO is similar in structure but not in sequence to [[Ubiquitin|ubiquitin]]. In several organisms SUMO is called SMT3. The SUMO-conjugating enzyme (E2) is called UBC9. The sentrin specific protease (SEPN) cleaves the C-terminal peptide from SUMO which then can bind to ubiquitin activating enzyme (E1). For details on SUMO-1 protein complex see <br /> | + | [[SUMO]] is a '''Small Ubiquitin-like MOdifier''' which covalently attaches to cellular proteins to modify their function. SUMO is similar in structure but not in sequence to [[Ubiquitin|ubiquitin]]. In several organisms SUMO is called '''SMT3'''. The SUMO-conjugating enzyme (E2) is called UBC9. The sentrin specific protease (SEPN) cleaves the C-terminal peptide from SUMO which then can bind to ubiquitin activating enzyme (E1). For details on SUMO-1 protein complex see <br /> |
*[[Human SUMO E1 complex]] <br /> | *[[Human SUMO E1 complex]] <br /> | ||
*[[Human SUMO E1 complex with a SUMO1-AMP mimic]]<br /> | *[[Human SUMO E1 complex with a SUMO1-AMP mimic]]<br /> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Reference
- ↑ Sarge KD, Park-Sarge OK. Sumoylation and human disease pathogenesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 2009 Apr;34(4):200-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.01.004. Epub, 2009 Mar 11. PMID:19282183 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2009.01.004
- ↑ Olsen SK, Capili AD, Lu X, Tan DS, Lima CD. Active site remodelling accompanies thioester bond formation in the SUMO E1. Nature. 2010 Feb 18;463(7283):906-12. PMID:20164921 doi:10.1038/nature08765